Breadcrumb

Biological souring and mitigation strategies in oil reservoirs
Biological souring is one of the major problems facing the oil and gas sector as a result of biogenic sulfide generation in the reservoirs. Sulfidogenic microorganism and particularly sulfate-reducing bacteria are the main generator of the biogenic sulfide. In consequence, souring has a plethora of economic and environmental problems. It has a negative impact on the petroleum industry, where the generated sulfide lowers air quality and causes adverse health problems due to its toxicity and carcinogenicity. Furthermore, it affects the whole industry by reducing the product quality and enhancing
Valorization of Agricultural and Marine Waste for Fabrication of Bio-Adsorbent Sheets
Industrial wastewater often contains considerable amounts of toxic pollutants that would endanger public health and the environment. In developing countries, these toxins are often discharged into natural ecosystems without pretreatment as it requires costly treatment processes, which causes long-term harmful socioeconomic impacts. Employing wastewater treatment plants using physical, biological, and chemical methods to clean the wastewater is considered by many nations the answer to the environmental crises. The treated water could be used for targeting the irrigation systems in its majority

Review on Coral Reef Regeneration Methods through Renewable Powered Electrotherapy
The restoration of coral reef population in coastal regions is currently a growing concern. Many attempts have been made to apply new approaches to limit the deterioration of coral reefs, and to accelerate the growth of new reefs to protect coastal areas and ecosystems using available renewable energy sources. This paper highlights the new approaches and their various advantages and limitations in tidal and wave energy. The paper also suggests improvements to some of those systems using the recent developments in soft robotics, especially the use of biomimetic fish as a feasible support

A collection of interdisciplinary applications of fractional-order circuits
An attractive feature of fractional calculus is its application in various interdisciplinary fields, extending from biomedical and biological notions to mechanical properties. For their description, fractional-order models have outperformed the corresponding integer-order models, resulting in a more realistic behavior, due to the additional degrees of freedom offered and the long-term memory effect that reflects the fractional order. These improved features are processed by appropriate circuit implementations, derived through several approximation methods, whose primary objective is to provide
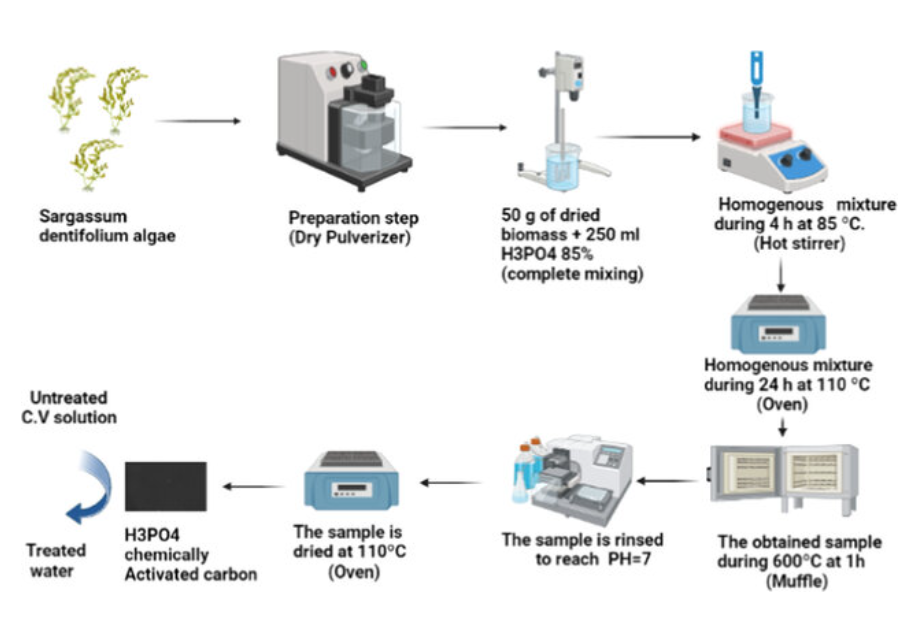
Crystal violet removal using algae-based activated carbon and its composites with bimetallic Fe0-Cu
The textile industry is considered a source of pollution because of the discharge of dye wastewater. The dye wastewater effluent has a significant impact on the aquatic environment. According to the World Bank, textile dyeing, and treatment contribute 17 to 20% of the pollution of water. This paper aims to prepare the bimetallic nano zero-valent iron-copper (Fe0-Cu), algae-activated carbon, and their composites (AC-Fe0-Cu), which are employed as adsorbents. In this paper, Synthetic adsorbents are prepared and examined for the adsorption and removal of soluble cationic crystal violet (CV) dye
A computational flow model of oxygen transport in the retinal network
The retina's high oxygen demands and the retinal vasculature's relatively sparse nature are assumed to contribute to the retina's specific vulnerability to vascular diseases. This study has been designed to model the oxygen transport in physiologically realistic retinal networks. A computational fluid dynamics study has been conducted to investigate the effect of topological changes on the oxygen partial pressure distribution in retinal blood vessels. The Navier Stokes equations for blood flow and the mass transport equation for oxygen have been coupled and solved simultaneously for the
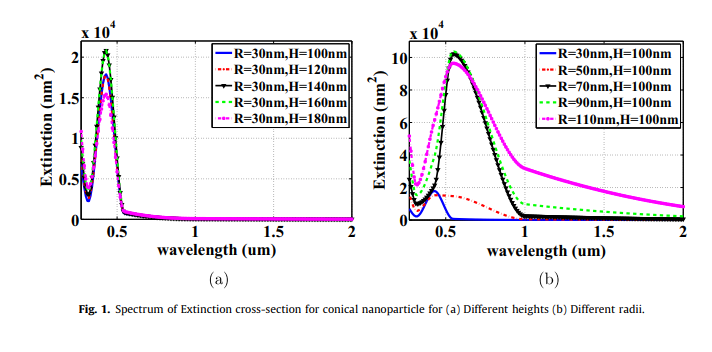
J-V characteristics of plasmonic photovoltaics with embedded conical and cylindrical metallic nanoparticles
Plasmonic photovoltaics (PVs) are promising structures that improve thin-film photovoltaics performance, where optical absorption is improved via embedding metallic nanoparticles in the PV's active layer to trap the incident optical wave into the photovoltaic cell. The presented work investigates the design of PV with both structures of conical and cylindrical metallic nanoparticles through studying their extinction cross-sections and electric field distributions. Also, the impact of these nanoparticles in silicon PVs on the optical absorption enhancement is investigated. The figure of merit
Further experimental evidence of the fractional-order energy equation in supercapacitors
Due to the dispersive porous nature of its material, carbon–carbon supercapacitors have a current–voltage relationship which is modeled by a fractional-order differential equation of the form i(t)=Cα[Formula presented] where α≤1 is a dispersion coefficient and Cα is a pseudo-capacitance not measurable in Farads. Hence, the energy stored in a capacitor, known to equal CV2/2 where C is the capacitance in Farad and V is the voltage applied, does not apply to a supercapacitor. In a recent work (Allagui et al., 2016), a fractional-order energy equation that enables the quantification of the energy
Fuzzy firefly clustering for tumour and cancer analysis
Swarm intelligence represents a meta-heuristic approach to solve a wide variety of problems. Searching for similar patterns of genes is becoming very essential to predict the expression of genes under various conditions. Firefly clustering inspired by the behaviour of fireflies helps in grouping genes that behave alike. Contrasting hard clustering methodology, fuzzy clustering assigns membership values for every gene and predicts the possibility of belonging to every cluster. To distinguish highly expressed and suppressed genes, the research in this paper proposes an efficient fuzzy-firefly
Fractional-order mathematical model for Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia
This paper is dedicated to develop a fractional order model of the rate of change of cancerous blood cells in Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia using fractional-order differential equations as well as tackling the factors that affect this rate and compare between them. The simulated cases (using MATLAB) prove that the proposed model is doable in terms of the variables positions in the equations and its effect on the overall population. Also, the effect of the Pactional order is investigated through three parameters sets and it has shown strong influence on the dynamic response. © 2017 IEEE.
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 4
- Next page ››
