Breadcrumb

Fractional-order inverse filters revisited: Equivalence with fractional-order controllers
The equivalence of fractional-order inverse filters with fractional-order controllers is demonstrated in this work. This is achieved by appropriately rewriting the filters transfer functions in order to clarify the correspondence between the gain and time-constant of the filters and the scaling factor and differentiation/integration constant of the controllers. Possible implementations of fractional-order inverse filters using second generation voltage conveyors are presented and an application example, related to the control of a motion system, is demonstrated for evaluating the behavior of
Di- and tri- cyclic aromatic hydrocarbons removal using different prepared materials based Sargassum dentifolium algae, and iron oxide
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are highly toxic and carcinogenic compounds as they are low water solubility, hardly degradable and may persist in the environment for many years. Therefore, this study was directed to PAHs ‘anthracene and naphthalene’ removal using a combination method between adsorption and degradation using sunlight. Three adsorbent materials, iron oxide (Fe) alone, Sargassum dentifolium (S) alone, and mixture of Iron oxide and Sargassum dentifolium (FeS) were prepared. Afterwards, optimisation process was performed for the three adsorbent forms through some
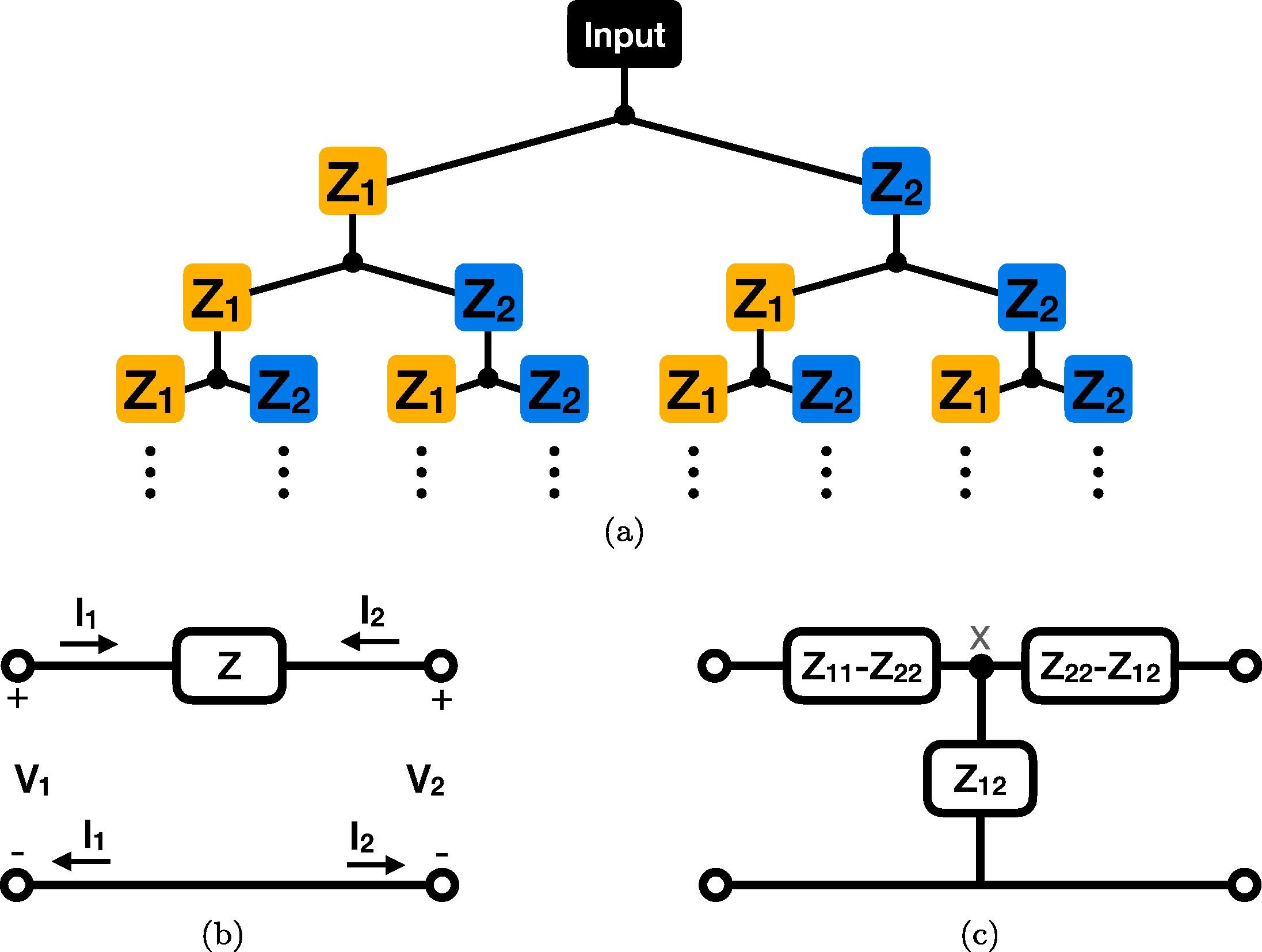
Generalizing the Warburg impedance to a Warburg impedance matrix
We seek to generalize and study the well-known Warburg impedance element, which has an impedance proportional to 1/s (s=jω is the complex frequency), to a two-port impedance network. For this purpose, we consider an infinite binary tree structure inside which each impedance is treated as a two-port network. We obtain a Warburg impedance matrix, which is both symmetrical and reciprocal, and study its equivalent circuit behavior. Interestingly, the equivalent circuit contains two resistors and a Cole–Davidson type impedance proportional to 1+2/(τs), where τ is a time constant. Simulation results
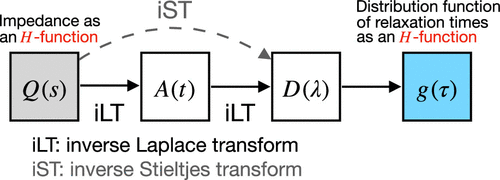
Procedure for Obtaining the Analytical Distribution Function of Relaxation Times for the Analysis of Impedance Spectra Using the Fox H-Function
The interpretation of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy data by fitting them to equivalent circuit models has been a standard method of analysis in electrochemistry. However, the inversion of the data from the frequency domain to a distribution function of relaxation times (DFRT) has gained considerable attention for impedance data analysis as it can reveal more detailed information about the underlying electrochemical processes without requiring a priori knowledge. The primary purpose of this paper is to provide a general and practical procedure for obtaining analytically the DFRT from
A computational flow model of oxygen transport in the retinal network
The retina's high oxygen demands and the retinal vasculature's relatively sparse nature are assumed to contribute to the retina's specific vulnerability to vascular diseases. This study has been designed to model the oxygen transport in physiologically realistic retinal networks. A computational fluid dynamics study has been conducted to investigate the effect of topological changes on the oxygen partial pressure distribution in retinal blood vessels. The Navier Stokes equations for blood flow and the mass transport equation for oxygen have been coupled and solved simultaneously for the
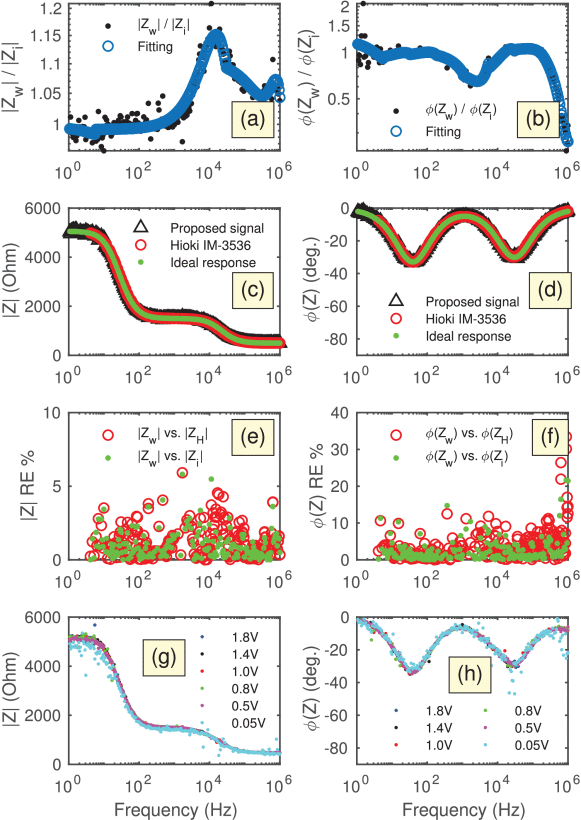
Time-Frequency Design of a Multi-Sine Excitation with Random Phase and Controllable Amplitude for (Bio) Impedance Measurements
Impedance spectroscopy has become a standard electroanalytical technique to study (bio)electrochemical and physiological systems. From an instrumentation point of view, the measurement of impedance can be carried out either in the frequency domain using the classical frequency sweep method or in the time domain using a variety of broadband signals. While time-domain techniques can be implemented with relatively simple hardware and can achieve faster acquisition time, they are still not that popular because of their lower accuracy and modularity. In this work we present a method and an
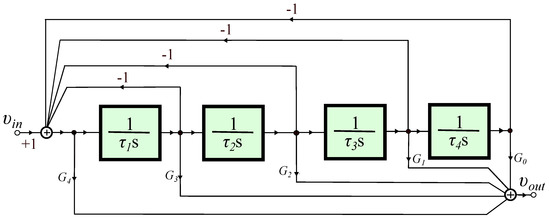
A 1 + α Order Generalized Butterworth Filter Structure and Its Field Programmable Analog Array Implementation
Fractional-order Butterworth filters of order 1 + (Formula presented.) (0
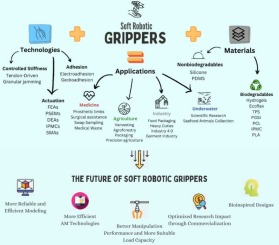
Soft robotic grippers: A review on technologies, materials, and applications
The growing need for manipulators capable of handling delicate objects with care and coexisting safely with humans has brought soft robots to the forefront as a practical and cost-effective solution. In this context, this paper aims to explore soft grippers, a unique and versatile subset of soft robots. It provides an overview of various soft grasping techniques and materials, highlighting their respective advantages and limitations, along with showcasing several designed and tested models. As medicine and agriculture are acknowledged as pivotal domains required for basic human survival, this
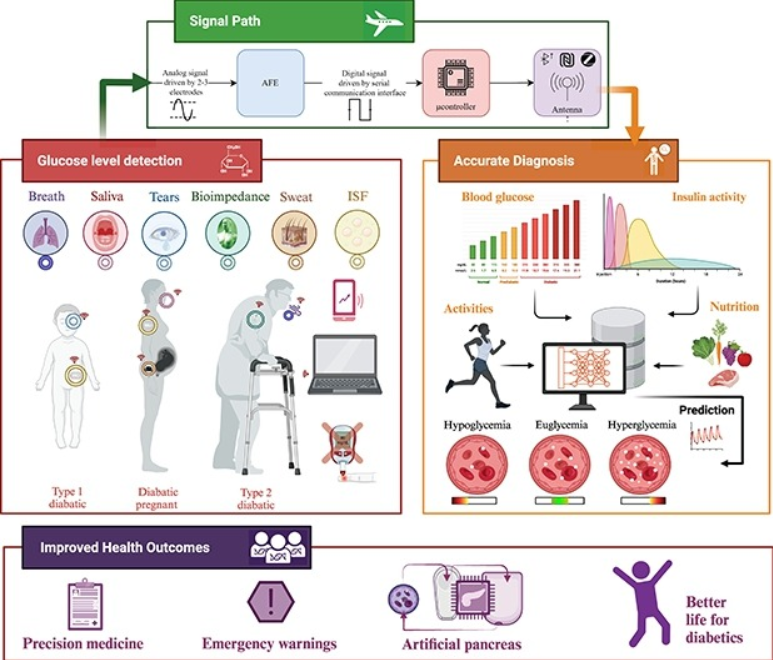
Wearable devices for glucose monitoring: A review of state-of-the-art technologies and emerging trends
Diabetes is a chronic condition that is characterized by high blood glucose levels and can cause damage to multiple organs over time. Continuous monitoring of glucose levels is essential for both diabetic and non-diabetic individuals. There have been major developments in glucose monitoring technology over the past decade, which have been driven by research and industry efforts. Despite these significant advancements, the area of glucose biosensors still faces significant challenges. This paper presents a comprehensive summary of the latest glucose monitoring technologies, including invasive
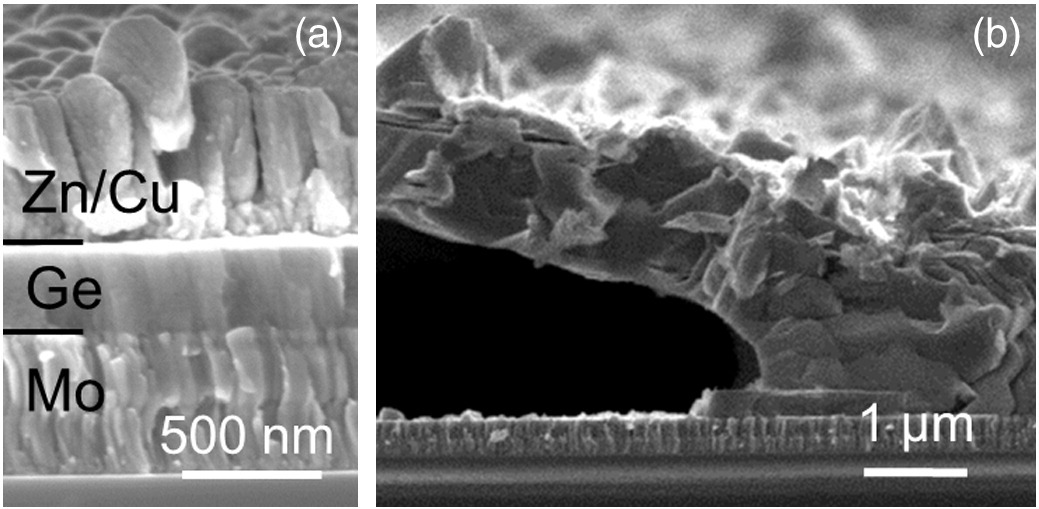
Physical characterization of Cu2ZnGeSe4thin films from annealing of Cu-Zn-Ge precursor layers
Cu2ZnGeSe4(CZGeSe) can be considered as a potential alternative for wide band gap thin film devices. In this work, CZGeSe thin films were deposited on Mo-coated soda lime glass substrates by sequential deposition of sputtered Cu, Zn and e-beam evaporated Ge layers from elemental targets followed by annealing at high temperature using H2Se gas. We report on the effect of the precursor stack order and composition and the impact of the annealing temperature on the physical properties of CZGeSe thin films. The optimal layer morphology was obtained when using a Mo/Cu/Zn/Ge precursor stack annealed
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 2
- Next page ››
