Breadcrumb

Preparation and Characterization of nZVI, Bimetallic Fe 0-Cu, and Fava Bean Activated Carbon-Supported Bimetallic AC-F e 0-Cu for Anionic Methyl Orange Dye Removal
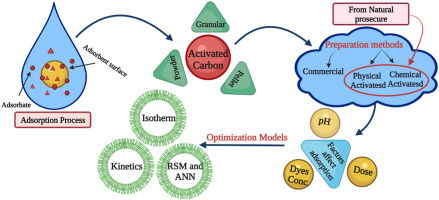
Review of activated carbon adsorbent material for textile dyes removal: Preparation, and modelling
Water contamination with colours and heavy metals from textile effluents has harmed the ecology and food chain, with mutagenic and carcinogenic effects on human health. As a result, removing these harmful chemicals is critical for the environment and human health. Various standard physicochemical and biological treatment technologies are used; however, there are still some difficulties. Adsorption is described as a highly successful technology for removing contaminants from textile-effluents wastewater compared to other methods. Several adsorbent materials, including nanomaterials, natural
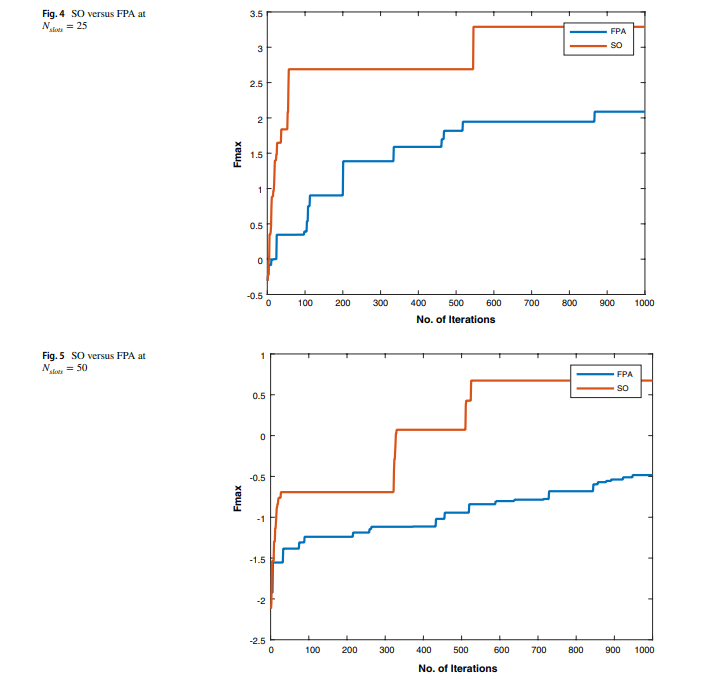
A power-aware task scheduler for energy harvesting-based wearable biomedical systems using snake optimizer
There is an increasing interest in energy harvesting for wearable biomedical devices. This requires power conservation and management to ensure long-term and steady operation. Hence, task scheduling algorithms will be used throughout this work to provide a reliable solution to minimize energy consumption while considering the system operation constraints. This study proposes a novel power-aware task scheduler to manage system operations. For example, we used the scheduler to handle system operations, including heart rate and temperature sensors. Two optimization techniques have been used to

Modified Blowfish Algorithm Based on Improved Lorenz Attractor
Image security becomes important topic because of increasing image usage in communication besides assures information security which is unseen in these images such as military and medical images. Blowfish is a superb symmetric cryptography that ensures a high degree of resistance to attacks. The proposed system modifies Blowfish algorithm by substituting the function in blowfish round with light weight function to save memory and resources of the platforms and Using 3-D chaotic system (Improved Lorenz) that work as a key timetable for creating Blowfish sub keys in order to increasing
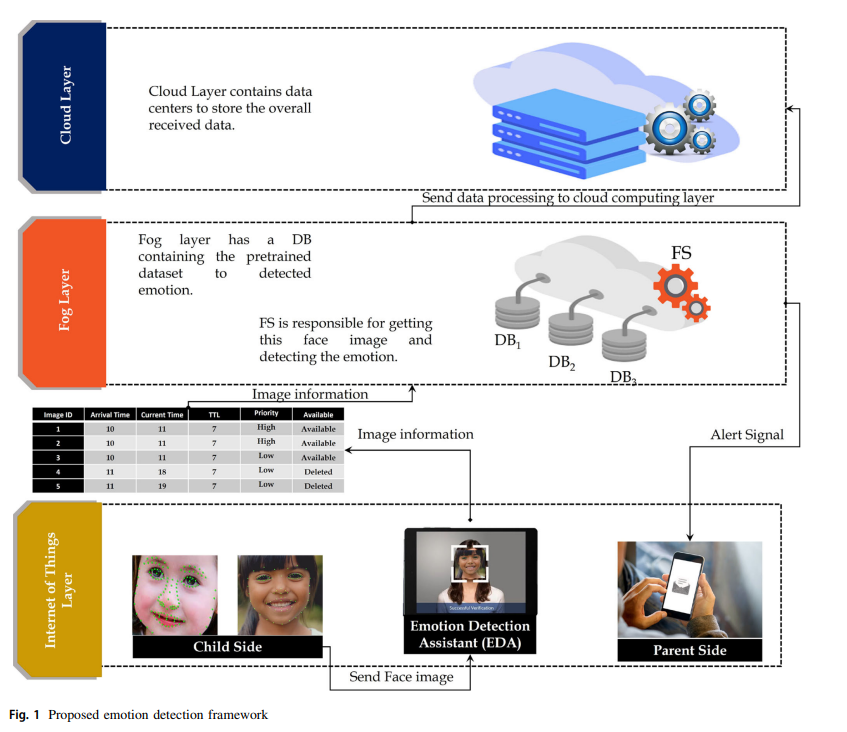
Real-time facial emotion recognition model based on kernel autoencoder and convolutional neural network for autism children
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder that is characterized by abnormalities in the brain, leading to difficulties in social interaction and communication, as well as learning and attention. Early diagnosis of ASD is challenging as it mainly relies on detecting abnormalities in brain function, which may not be evident in the early stages of the disorder. Facial expression analysis has shown promise as an alternative and efficient solution for early diagnosis of ASD, as children with ASD often exhibit distinctive patterns that differentiate them from typically
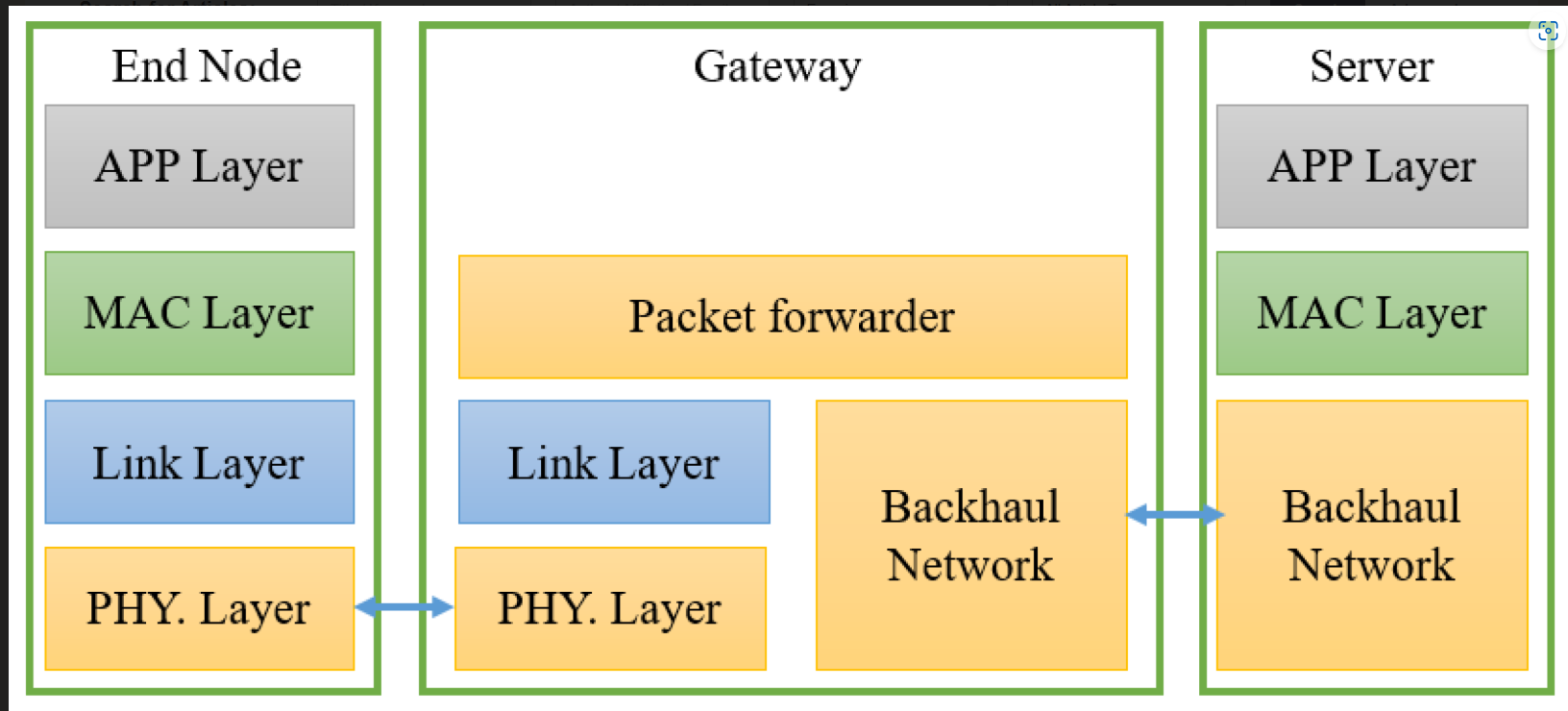
Internet of Things: A Comprehensive Overview on Protocols, Architectures, Technologies, Simulation Tools, and Future Directions
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a global network of interconnected computing, sensing, and networking devices that can exchange data and information via various network protocols. It can connect numerous smart devices thanks to recent advances in wired, wireless, and hybrid technologies. Lightweight IoT protocols can compensate for IoT devices with restricted hardware characteristics in terms of storage, Central Processing Unit (CPU), energy, etc. Hence, it is critical to identify the optimal communication protocol for system architects. This necessitates an evaluation of next-generation
Biologically Inspired Optimization Algorithms for Fractional-Order Bioimpedance Models Parameters Extraction
This chapter introduces optimization algorithms for parameter extractions of three fractional-order circuits that model bioimpedance. The Cole-impedance model is investigated; it is considered one of the most commonly used models providing the best fit with the measured data. Two new models are introduced: the fractional Hayden model and the fractional-order double-shell model. Both models are the generalization of their integer-order counterpart. These fractional-order models provide an improved description of observed bioimpedance behavior. New metaheuristic optimization algorithms for

Design Of Step Pyramidal Nanoparticle For Plasmonic Photovoltaics
Plasmonic Photovoltaics (PVs) are an effective method for increasing optical absorption by adding metallic nanoparticles to the photovoltaic active layer. The role of these nanoparticles is confining the incident light near them in the PV cell, resulting in thin film PVs of enhanced efficiency. Therefore, different materials and new NPs shapes are used for this purpose. In this research, a step pyramid is introduced as a novel structure for nanoparticles for enhancing plasmonic PVs by embedding an array of the proposed step pyramid nanoparticles within the PV cell. Therefore, the extinction

Fractional order systems: An overview of mathematics, design, and applications for engineers
Fractional Order Systems: An Overview of Mathematics, Design, and Applications for Engineers introduces applications from a design perspective, helping readers plan and design their own applications. The book includes the different techniques employed to design fractional-order systems/devices comprehensively and straightforwardly. Furthermore, mathematics is available in the literature on how to solve fractional-order calculus for system applications. This book introduces the mathematics that has been employed explicitly for fractional-order systems. It will prove an excellent material for
Accelerated Edge Detection Algorithm for High-Speed Applications
Digital Image Processing (DIP) is a growing field for various applications, such as autonomous vehicles and video surveillance. To improve the performance of DIP systems, image processing algorithms are implemented in hardware rather than software. The idea here is primarily to get a faster system than software imaging or other alternative hardware. Field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs) have the advantages of parallel processing, low cost, and low power consumption. These semiconductor devices contain many logic blocks that can be programmed to perform everything from basic digital gate-level
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 3
- Next page ››
