Breadcrumb
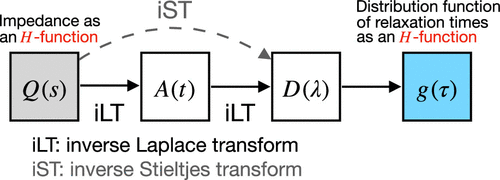
Procedure for Obtaining the Analytical Distribution Function of Relaxation Times for the Analysis of Impedance Spectra Using the Fox H-Function
The interpretation of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy data by fitting them to equivalent circuit models has been a standard method of analysis in electrochemistry. However, the inversion of the data from the frequency domain to a distribution function of relaxation times (DFRT) has gained considerable attention for impedance data analysis as it can reveal more detailed information about the underlying electrochemical processes without requiring a priori knowledge. The primary purpose of this paper is to provide a general and practical procedure for obtaining analytically the DFRT from
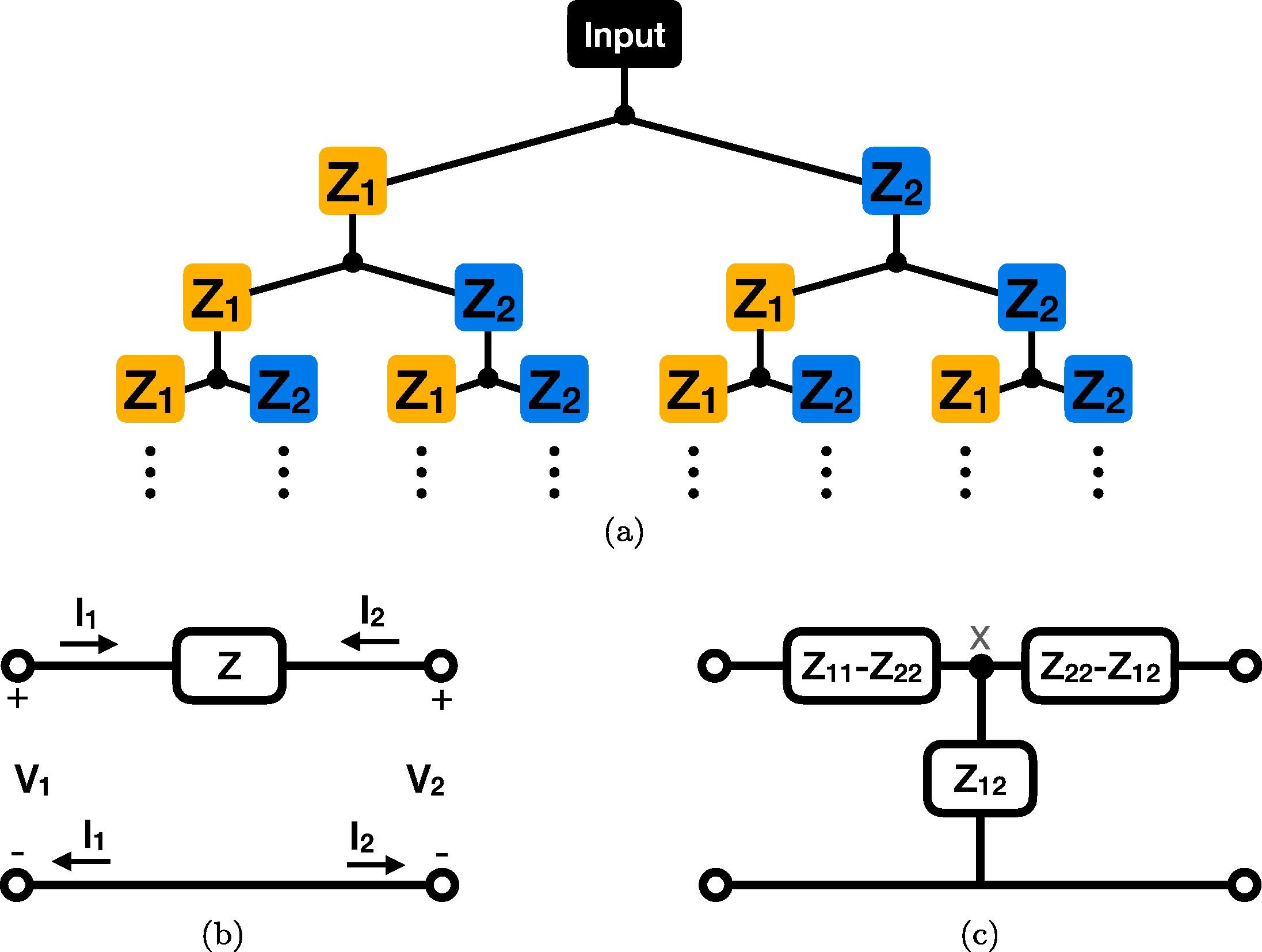
Generalizing the Warburg impedance to a Warburg impedance matrix
We seek to generalize and study the well-known Warburg impedance element, which has an impedance proportional to 1/s (s=jω is the complex frequency), to a two-port impedance network. For this purpose, we consider an infinite binary tree structure inside which each impedance is treated as a two-port network. We obtain a Warburg impedance matrix, which is both symmetrical and reciprocal, and study its equivalent circuit behavior. Interestingly, the equivalent circuit contains two resistors and a Cole–Davidson type impedance proportional to 1+2/(τs), where τ is a time constant. Simulation results

A note on the bandwidth of negative group delay filters
An updated definition of group delay bandwidth in analog filters is introduced in this work. Unlike existing definitions, this new definition considers simultaneously the value of the group delay and filter gain, leading to minimized distortion in the filter output. In addition, it offers the capability of handling wide-band signals without introducing errors in the shape of their envelopes. Selected first- and second-order filters are studied and simulation results are provided to validate the efficiency of the new definition. © 2024 The Author(s). International Journal of Circuit Theory and

Fractional-order inverse filters revisited: Equivalence with fractional-order controllers
The equivalence of fractional-order inverse filters with fractional-order controllers is demonstrated in this work. This is achieved by appropriately rewriting the filters transfer functions in order to clarify the correspondence between the gain and time-constant of the filters and the scaling factor and differentiation/integration constant of the controllers. Possible implementations of fractional-order inverse filters using second generation voltage conveyors are presented and an application example, related to the control of a motion system, is demonstrated for evaluating the behavior of

Synthesis of resonance-based common-gate fully differential band-pass filters
We propose a class of fully differential filters based on a common-gate differential amplifier cell in three different topologies. Our focus is on the synthesis of second-order band-pass filters and we found 53 possible circuits. All filters are resonance-based and have electronically tunable gain. Post layout simulations in 65-nm CMOS technology are provided to validate the proper function of these filters. © 2022 Elsevier B.V.

Tikhonov regularization for the deconvolution of capacitance from the voltage–charge response of electrochemical capacitors
The capacitance of capacitive energy storage devices cannot be directly measured, but can be estimated from the applied input and measured output signals expressed in the time or frequency domains. Here the time-domain voltage–charge relationship of non-ideal electrochemical capacitors is treated as an ill-conditioned convolution integral equation where the unknown capacitance kernel function is to be found. This comes from assuming a priori that in the frequency domain the charge is equal to the product of capacitance by voltage, which is in line with the definition of electrical impedance
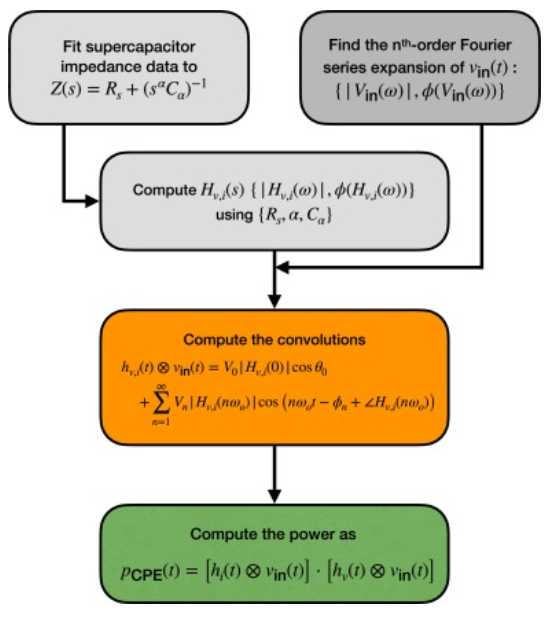
Time-domain response of supercapacitors using their impedance parameters and Fourier series decomposition of the excitation signal
Supercapacitors are mostly recognized for their high power density capabilities and fast response time when compared to secondary batteries. However, computing their power in response to a given excitation using the standard formulæof capacitors is misleading and erroneous because supercapacitors are actually non-ideal capacitive devices that cannot be characterized with a single constant capacitance. In this study we show how to estimate accurately the time-domain power and energy of supercapacitors in response to any excitation signal represented in terms of its Fourier series coefficients

Approximation and realization of power-law all-pass filters
Non-integer power-law all-pass transfer functions, are approximated by suitable integer-order transfer functions in this work. The derivation of the integer-order transfer functions is based on the analytic expansion of the (non-integer) power-law transfer functions through the utilization of the binomial theorem. The offered benefit is the derivation of stable integer-order transfer functions. This study is supported by experimental results, obtained using a Field Programmable Analog Array device, after the employment of curve fitting based approximation techniques. © 2022 Elsevier GmbH
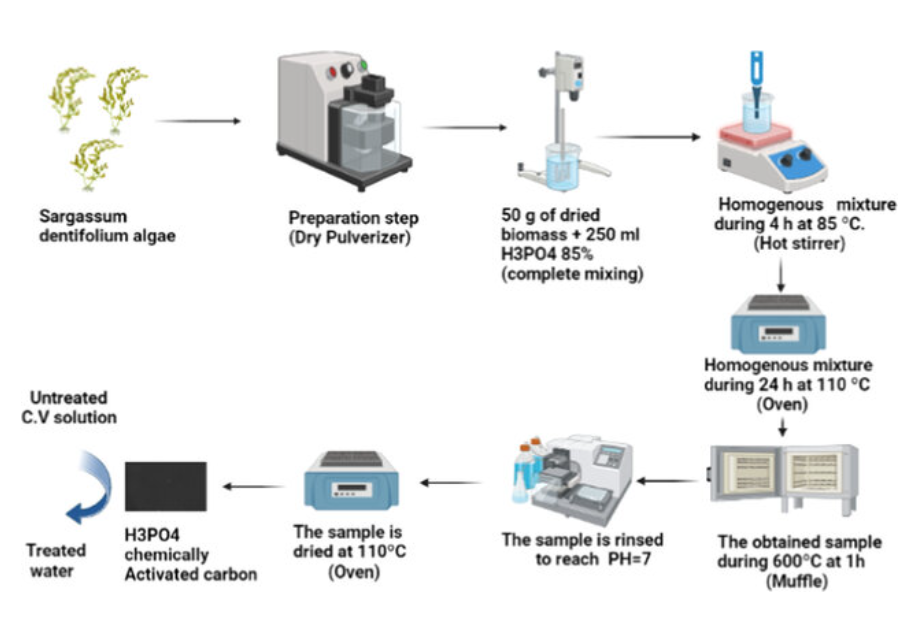
Crystal violet removal using algae-based activated carbon and its composites with bimetallic Fe0-Cu
The textile industry is considered a source of pollution because of the discharge of dye wastewater. The dye wastewater effluent has a significant impact on the aquatic environment. According to the World Bank, textile dyeing, and treatment contribute 17 to 20% of the pollution of water. This paper aims to prepare the bimetallic nano zero-valent iron-copper (Fe0-Cu), algae-activated carbon, and their composites (AC-Fe0-Cu), which are employed as adsorbents. In this paper, Synthetic adsorbents are prepared and examined for the adsorption and removal of soluble cationic crystal violet (CV) dye

Reduce Computing Complexity of Deep Neural Networks Through Weight Scaling
Large deep neural network (DNN) models are computation and memory intensive, which limits their deployment especially on edge devices. Therefore, pruning, quantization, data sparsity and data reuse have been applied to DNNs to reduce memory and computation complexity at the expense of some accuracy loss. The reduction in the bit-precision results in loss of information, and the aggressive bit-width reduction could result in noticeable accuracy loss. This paper introduces Scaling-Weight-based Convolution (SWC) technique to reduce the DNN model size and the complexity and number of arithmetic
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 4
- Next page ››
