Breadcrumb

In-Memory Associative Processors: Tutorial, Potential, and Challenges
In-memory computing is an emerging computing paradigm that overcomes the limitations of exiting Von-Neumann computing architectures such as the memory-wall bottleneck. In such paradigm, the computations are performed directly on the data stored in the memory, which highly reduces the memory-processor communications during computation. Hence, significant speedup and energy savings could be achieved especially with data-intensive applications. Associative processors (APs) were proposed in the seventies and recently were revived thanks to the high-density memories. In this tutorial brief, we
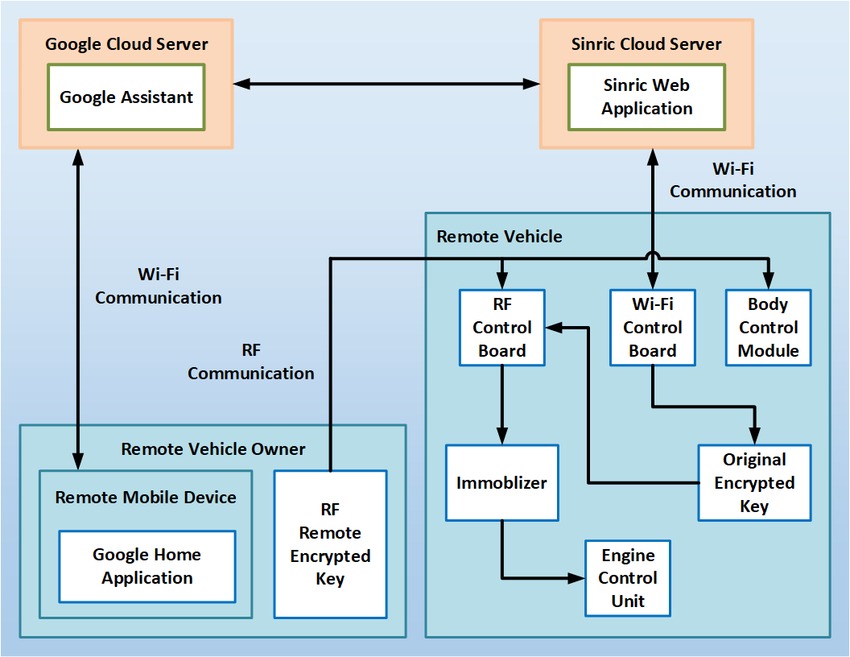
A Reliable Secure Architecture for Remote Wireless Controlling of Vehicle's Internal Systems based on Internet of Vehicles using RF and Wi-Fi
Internet of Vehicles is considered one of the most unprecedented outputs of the Internet of Things. No one has realized or even expected the rapidly-growing revolution regarding autonomous connected vehicles. Nowadays, Internet of Vehicles is massively progressing from Vehicular Ad-Hoc Networks as a huge futuristic research and development discipline. This paper proposes a novel reliable and secure architecture for ubiquitously controlling remote connected cars' internal systems, such as engine, doors' locks, sunroof, horn, windows' and lights' control systems. The main contribution is that
Retraction Note: Hybrid rough-bijective soft set classification system (Neural Computing and Applications, (2018), 29, 8, (67-78), 10.1007/s00521-016-2711-z)
Retraction to: Neural Comput & Applic (2018) 29:67–78https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2711-z. The Editor-in-Chief and the publisher have retracted this article. The article was submitted to be part of a guest-edited issue. An investigation by the publisher found a number of articles, including this one, with a number of concerns, including but not limited to compromised editorial handling and peer review process, inappropriate or irrelevant references or not being in scope of the journal or guest-edited issue. Based on the investigation’s findings the Editor-in-Chief therefore no longer has

On the Theory and Application of the Fractional-Order Dirac-Delta Function
In this brief, we study a generalized fractional-order Dirac delta function defined using the M-Wright function Mα (t). The function Mα (t) is the inverse Laplace transform of the single- parameter Mittag-Leffler function Eα (−s), which itself can be viewed as the fractional-order generalization of the exponential function for 0
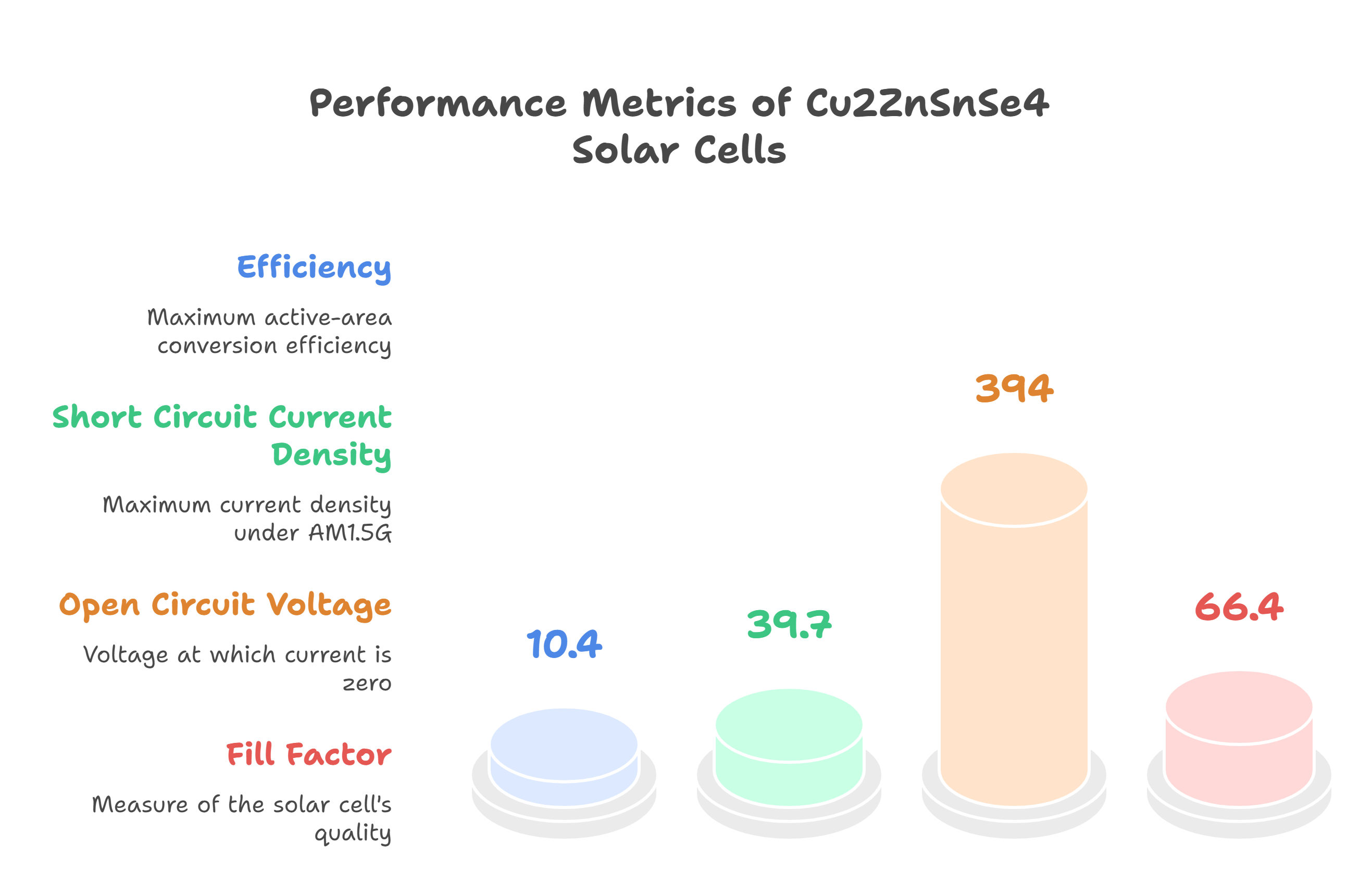
Physical and electrical characterization of high-performance Cu2ZnSnSe4based thin film solar cells
We report on the electrical, optical and physical properties of Cu2ZnSnSe4solar cells using an absorber layer fabricated by selenization of sputtered Cu, Zn and Cu10Sn90multilayers. A maximum active-area conversion efficiency of 10.4% under AM1.5G was measured with a maximum short circuit current density of 39.7 mA/cm2, an open circuit voltage of 394 mV and a fill factor of 66.4%. We perform electrical and optical characterization using photoluminescence spectroscopy, external quantum efficiency, current-voltage and admittance versus temperature measurements in order to derive information

Elementary Negative Group Delay Filter Functions
A theoretical study of the behavior of some elementary first- and second-order functions, which are suitable for realizing negative group delay, is performed in this work. As both the gain and phase responses are simultaneously considered, important derivations related to the actual bandwidth of operation are derived accompanied by useful design tips. The presented theory is supported by simulation and experimental results obtained through the utilization of typical active-RC filter structures, as well as from a field-programmable analog array device. © The Author(s) 2024.
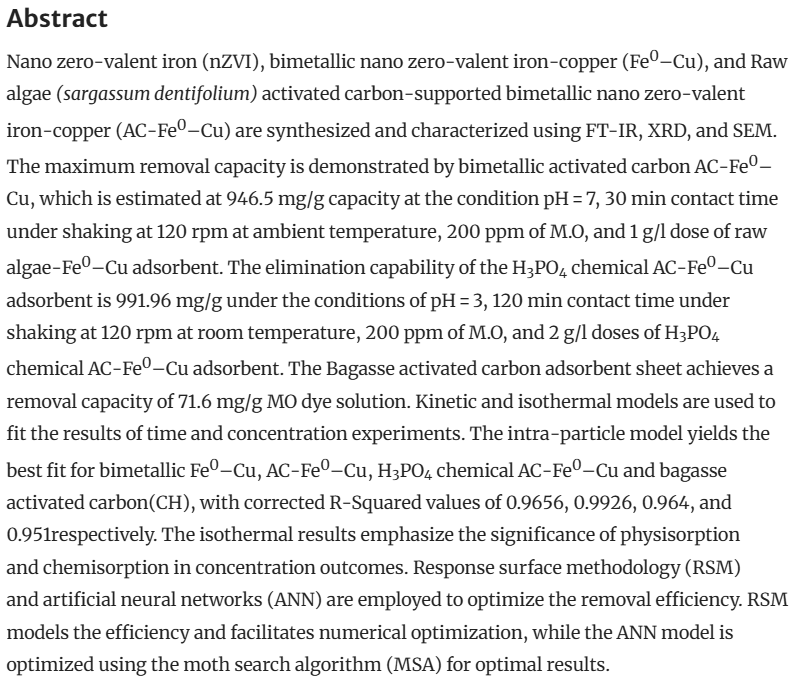
Bio-inspired adsorption sheets from waste material for anionic methyl orange dye removal
Abstract: Nano zero-valent iron (nZVI), bimetallic nano zero-valent iron-copper (Fe0–Cu), and Raw algae (sargassum dentifolium) activated carbon-supported bimetallic nano zero-valent iron-copper (AC-Fe0–Cu) are synthesized and characterized using FT-IR, XRD, and SEM. The maximum removal capacity is demonstrated by bimetallic activated carbon AC-Fe0–Cu, which is estimated at 946.5 mg/g capacity at the condition pH = 7, 30 min contact time under shaking at 120 rpm at ambient temperature, 200 ppm of M.O, and 1 g/l dose of raw algae-Fe0–Cu adsorbent. The elimination capability of the H3PO4
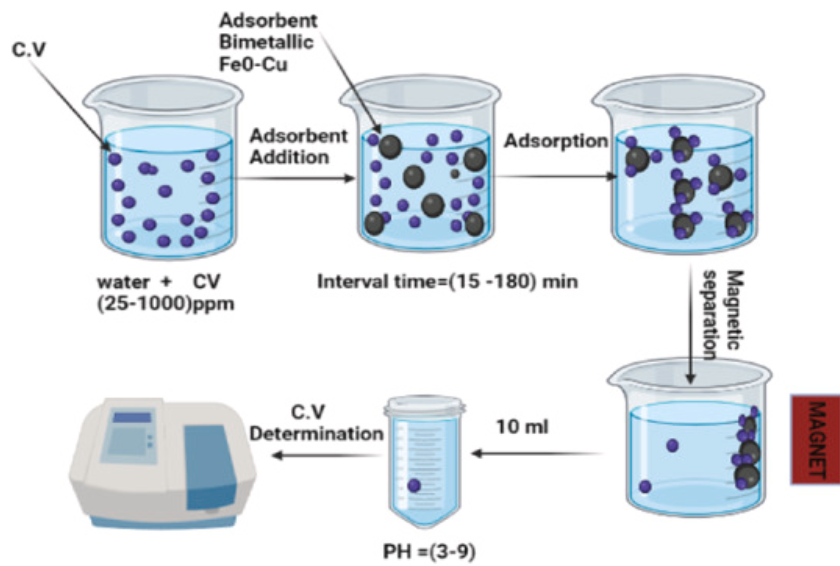
Crystal violet removal using bimetallic Fe0–Cu and its composites with fava bean activated carbon
Nano zero-valent iron (nZVI), bimetallic nano zero-valent iron-copper (Fe0– Cu), and fava bean activated carbon-supported bimetallic nano zero-valent iron-copper (AC-Fe0-Cu) are synthesized and characterized using DLS, zeta potential, FT-IR, XRD, and SEM. The maximum removal capacity is demonstrated by bimetallic Fe0–Cu, which is estimated at 413.98 mg/g capacity at pH 7, 180 min of contact duration, 120 rpm shaking speed, ambient temperature, 100 ppm of C.V. dye solution, and 1 g/l dosage. The elimination capability of the H2SO4 chemical AC-Fe0-Cu adsorbent is 415.32 mg/g under the same
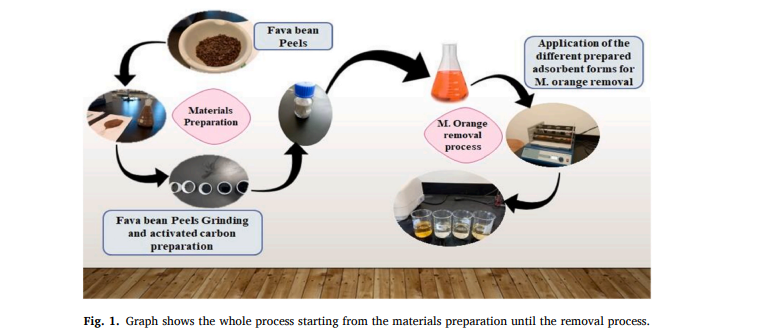
Experimental investigation of methyl-orange removal using eco-friendly cost-effective materials raw fava bean peels and their formulated physical, and chemically activated carbon
The discharge of effluents from dye industries into water streams poses a significant environmental and public health risk. In response, eco-friendly adsorbents derived from agricultural waste, such as Fava Bean Peels (R–FBP), have been investigated as potential materials for the removal of such pollutants. In this study, R–FBP and their corresponding physical and chemically activated carbon (P-RFB-AC and C-FBP-AC) were synthesized using H3PO4 acid and characterized using FT-IR, and SEM analyses. An optimization process was conducted to determine the optimum conditions for achieving high

Biological souring and mitigation strategies in oil reservoirs
Biological souring is one of the major problems facing the oil and gas sector as a result of biogenic sulfide generation in the reservoirs. Sulfidogenic microorganism and particularly sulfate-reducing bacteria are the main generator of the biogenic sulfide. In consequence, souring has a plethora of economic and environmental problems. It has a negative impact on the petroleum industry, where the generated sulfide lowers air quality and causes adverse health problems due to its toxicity and carcinogenicity. Furthermore, it affects the whole industry by reducing the product quality and enhancing
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 12
- Next page ››
