Breadcrumb
Artificial neural network for PWM rectifier direct power control and DC voltage control
In this chapter, a new technique has been proposed for reducing the harmonic content of a three-phase PWM rectifier connected to the networks with a unit power factor and also providing decoupled control of the active and reactive instantaneous power. This technique called direct power control (DPC) is based on artificial neural network (ANN) controller, without line voltage sensors. The control technique is based on well-known direct torque control (DTC) ideas for the induction motor, which is applied to eliminate the harmonic of the line current and compensate for the reactive power. The
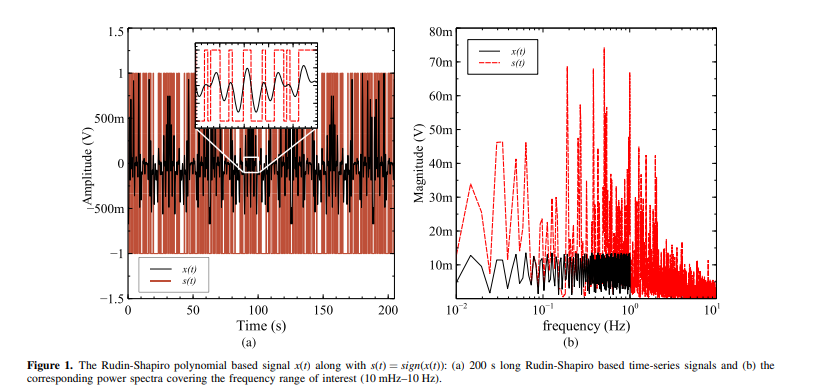
Electrical Impedance Spectroscopy Using a Wide-Band Signal Based on the Rudin-Shapiro Polynomials
Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) has become an increasingly important diagnostic and monitoring tool in many industries. An obstacle that arises when employing EIS in low and ultra low sub-Hz frequencies is the long measurement time associated with using the conventional frequency-sweep method. One possible solution to this problem is to use wide-band signals that cover at once the entire frequency range of interest. In this work, we explore and validate the use of such a signal obtained from the Rudin-Shapiro polynomial over the frequency range 10 mHz to 10 Hz. The proposed signal
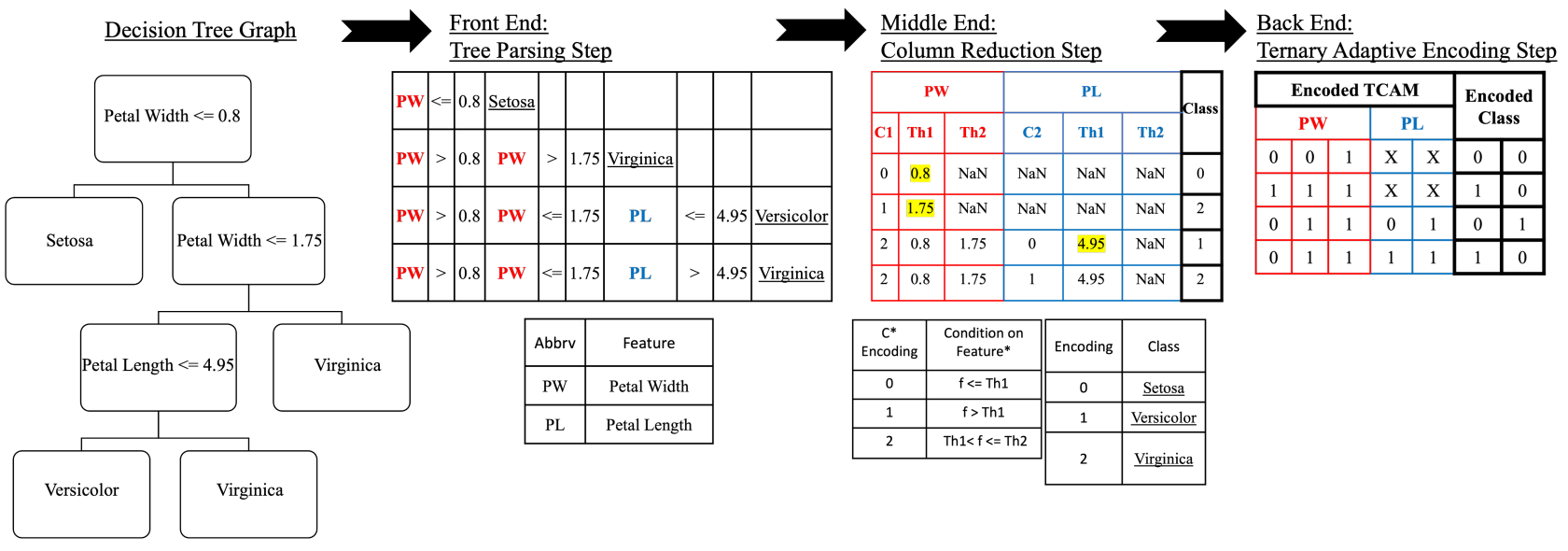
DT2CAM: A Decision Tree to Content Addressable Memory Framework
Decision trees are powerful tools for data classification. Accelerating the decision tree search is crucial for on-the-edge applications with limited power and latency budget. In this article, we propose a content-addressable memory compiler for decision tree inference acceleration. We propose a novel 'adaptive-precision' scheme that results in a compact implementation and enables an efficient bijective mapping to ternary content addressable memories while maintaining high inference accuracies. We also develop a resistive-based functional synthesizer to map the decision tree to resistive
Deep Learning Based Kinematic Modeling of 3-RRR Parallel Manipulator
This paper presents a novel low cost design for a 3-RRR Planar Parallel Manipulator (PPM). These manipulators proved their superiority over serial manipulators due to their speed, precision and smaller work space where the work space area is accounted for in the design to ensure that the robot is performing its task in a smooth and simple way without getting into any singularity points. The challenge with PPM is to obtain the kinematic constraint equations of the manipulator due to their complex non-linear behavior. Screw theory is a new approach that is used to compute the direct and inverse

Commercial Versus Natural Activated Carbon Fabricated Sheets: Applied to Dyes Removal Application
Industrial dyes are considered one of the main causes of increased water pollution of water. Many businesses, such as steel and paper, are located along riverbanks because they require large amounts of water in their manufacturing processes, and their wastes, which contain acids, alkalis, dyes, and other chemicals, are dumped and poured into rivers as effluents. For example, chemical enterprises producing aluminum emit a significant quantity of fluoride into the air and effluents into water bodies. Fertilizer facilities produce a lot of ammonia, whereas steel plants produce cyanide. Many
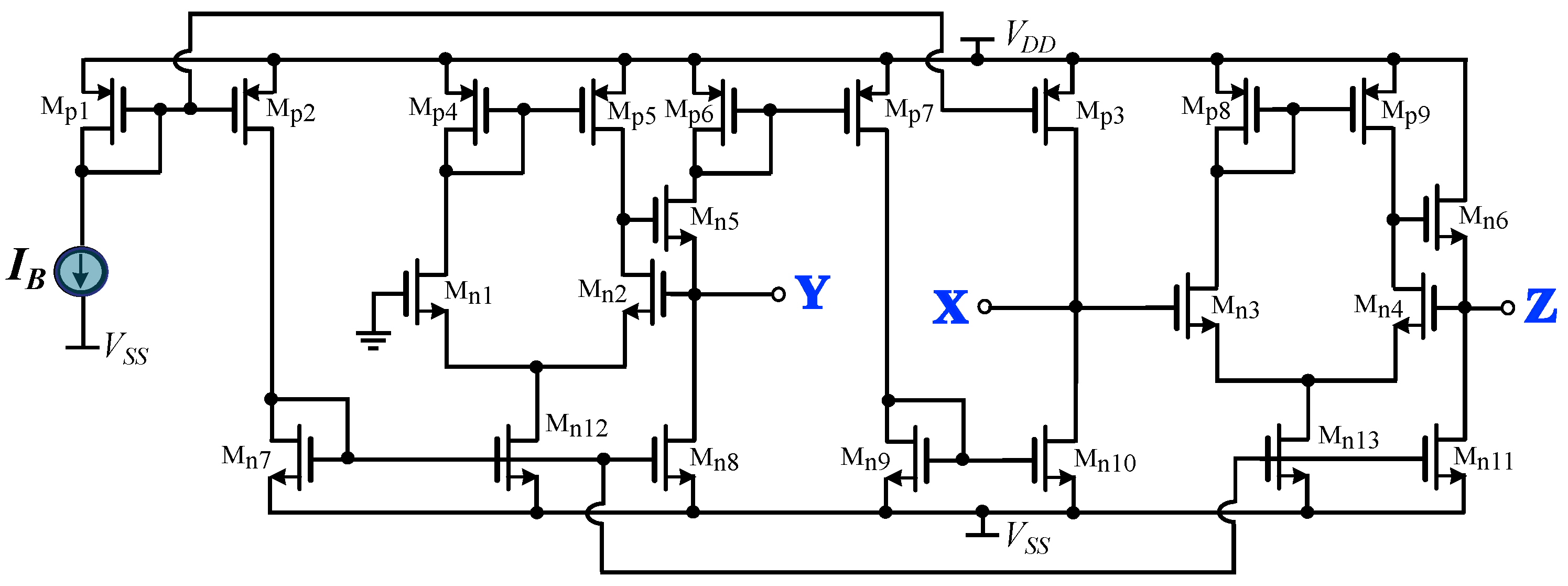
Minimum Active Component Count Design of a PIλDμ Controller and Its Application in a Cardiac Pacemaker System †
A generalized structure for implementing fractional-order controllers is introduced in this paper. This is achieved thanks to the consideration of the controller transfer function as a ratio of integer and non-integer impedances. The non-integer order impedance is implemented using RC networks, such as the Foster and Cauer networks. The main offered benefit, with regards to the corresponding convectional implementations, is the reduced active and, also, passive component count. To demonstrate the versatility of the proposed concept, a controller suitable for implementing a cardiac pacemaker

A note on the bandwidth of negative group delay filters
An updated definition of group delay bandwidth in analog filters is introduced in this work. Unlike existing definitions, this new definition considers simultaneously the value of the group delay and filter gain, leading to minimized distortion in the filter output. In addition, it offers the capability of handling wide-band signals without introducing errors in the shape of their envelopes. Selected first- and second-order filters are studied and simulation results are provided to validate the efficiency of the new definition. © 2024 The Author(s). International Journal of Circuit Theory and
Enhanced removal of crystal violet using rawfava bean peels, its chemically activated carbon compared with commercial activated carbon
Crystal violet is a basic dye that is widely used by various industries, such as textiles and paints. These industries discharge their effluents, contaminated with crystal violet, into water streams, and these effluents have an adverse effect on aquatic organisms, the environment, and human health. Crystal violet is a basic dye that is widely used by various industries, such as textiles and paints. These industries discharge their effluents, contaminated with crystal violet, into water streams, and these effluents have an adverse effect on aquatic organisms, the environment, and human health
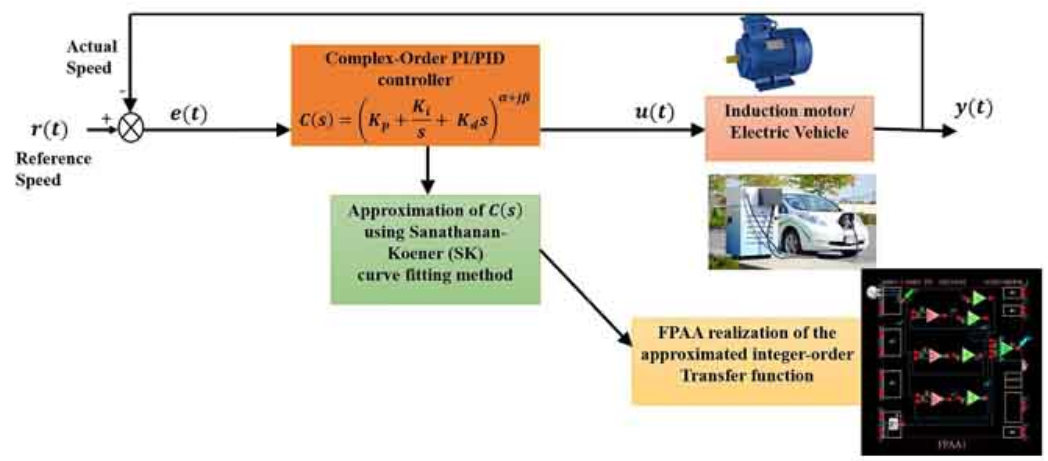
Design of Complex-Order PI/PID Speed Controllers and its FPAA Realization
Complex-order controllers are a generalized version of conventional integer-order controllers and are known to offer greater flexibility, better robustness, and improved system performance. This paper discusses the design of complex-order PI/PID controllers to control the speed of an induction motor drive and an electric vehicle. The speed-tracking performance of the complex-order controllers is compared with fractional-order controllers and conventional integer-order controllers. Implementing complex-order controllers is challenging due to commercial complex-order fractance element
Voltage-controlled M-M relaxation Oscillator
This paper discusses voltage-controlled M-M relaxation oscillator with analytical and circuit simulations. The introduced circuit has two different configurations based on the polarities of memristor; whether they are in the same direction or in the opposite direction. The Analytical formulas are function of the reference voltage such as the oscillation frequency and oscillation conditions for each case are derived with some numerical examples. The circuit simulations are introduced to validate the mathematical concepts as well as the effect of the reference voltage which can be used in
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 11
- Next page ››
