Breadcrumb
On the Design Flow of the Fractional-Order Analog Filters Between FPAA Implementation and Circuit Realization
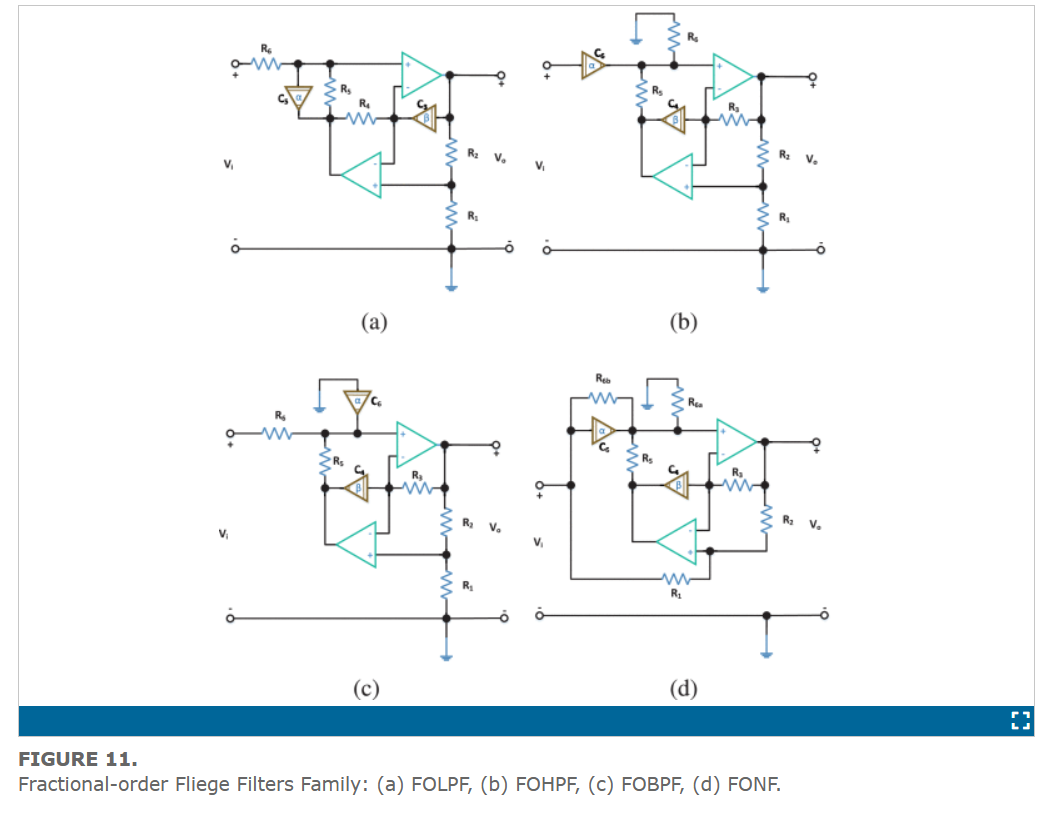
This work explicitly states the design flows of the fractional-order analog filters used by researchers throughout the literature. Two main flows are studied: the FPAA implementation and the circuit realization. Partial-fraction expansion representation is used to prepare the approximated fractional-order response for implementation on FPAA. The generalization of the second-order active RC analog filters based on opamp from the integer-order domain to the fractional-order domain is presented. The generalization is studied from both mathematical and circuit realization points of view. It is
FPGA Implementation of Reconfigurable CORDIC Algorithm and a Memristive Chaotic System with Transcendental Nonlinearities
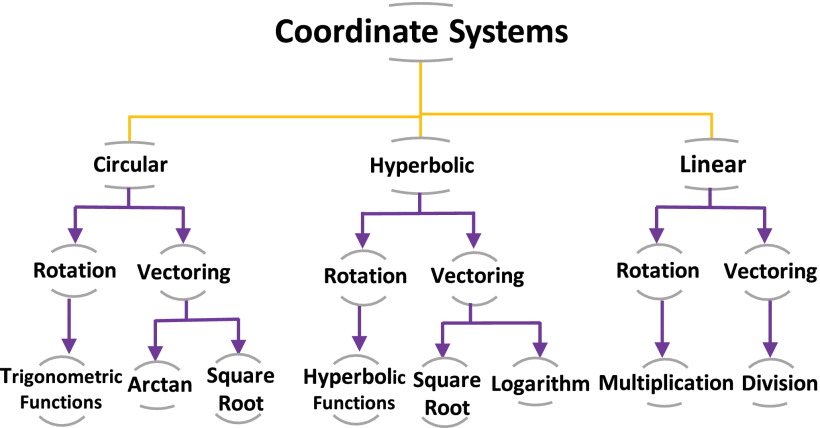
Coordinate Rotation Digital Computer (CORDIC) is a robust iterative algorithm that computes many transcendental mathematical functions. This paper proposes a reconfigurable CORDIC hardware design and FPGA realization that includes all possible configurations of the CORDIC algorithm. The proposed architecture is introduced in two approaches: multiplier-less and single multiplier approaches, each with its advantages. Compared to recent related works, the proposed implementation overpasses them in the included number of configurations. Additionally, it demonstrates efficient hardware utilization
On the fractional order generalized discrete maps
Chaos theory describes the dynamical systems which exhibit unpredictable, yet deterministic, behavior. Chaotic systems have a remarkable importance in both modeling and information processing in many fields. Fractional calculus has also become a powerful tool in describing the dynamics of complex systems such as fractional order (FO) chaotic systems. The FO parameter adds extra degrees of freedom which increases the design flexibility and adds more control on the design. The extra parameters increase the chaotic range. This chapter provides a review of several generalized discrete time one
Chaotic neural network quantization and its robustness against adversarial attacks
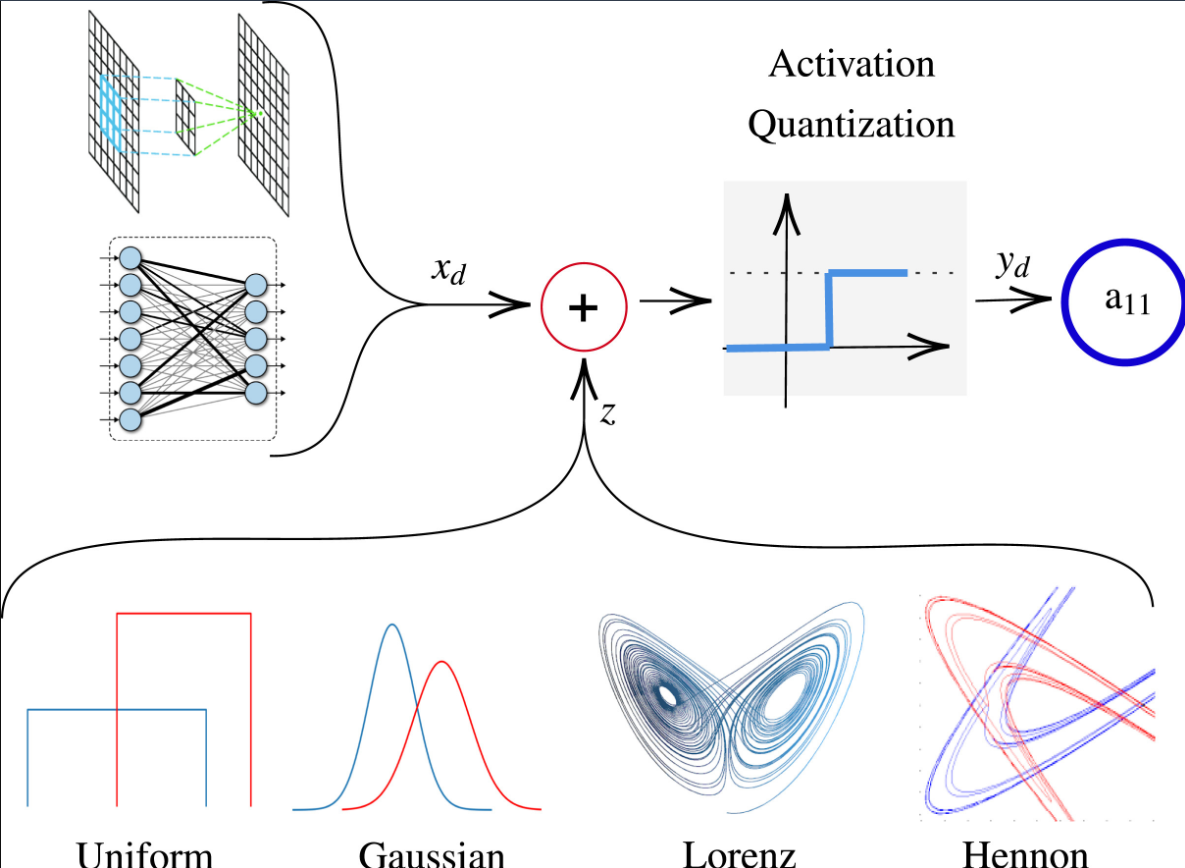
Achieving robustness against adversarial attacks while maintaining high accuracy remains a critical challenge in neural networks. Parameter quantization is one of the main approaches used to compress deep neural networks to have less inference time and less storage memory size. However, quantization causes severe degradation in accuracy and consequently in model robustness. This work investigates the efficacy of stochastic quantization to enhance robustness and accuracy. Noise injection during quantization is explored to understand the impact of noise types and magnitudes on model performance
On the Approximation of Fractional-Order Circuit Design
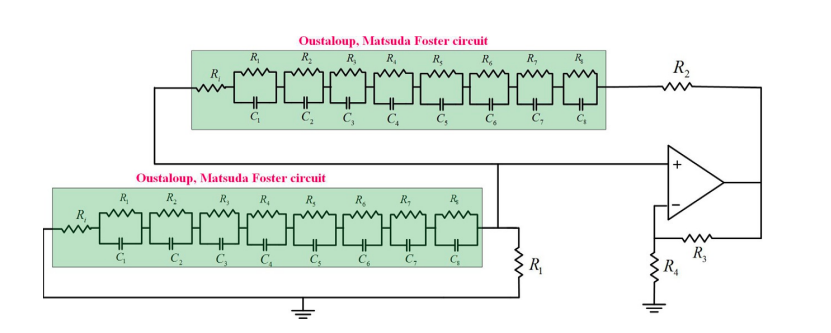
Despite the complex nature of fractional calculus, it is still fairly possible to reduce this complexity by using integer-order approximation. Each integer-order approximation has its own trade-offs from the complexity, sensitivity, and accuracy points of view. In this chapter, two different fractional-order electronic circuits are studied: the Wien oscillator and the CCII-based KHN filter with two different fractional elements of orders α and β. The investigation is concerned with changes in the response of these two circuits under two approximations: Oustaloup and Matsuda. A detailed review
A Unified System for Encryption and Multi-Secret Image Sharing Using S-box and CRT
Multi-Secret Image Sharing (MSIS) is used when multiple images need to be shared to multiple participants, but the images can not be recovered without the presence of all shares. In this paper, a unified system for performing encryption and (n,n)-MSIS is proposed. While MSIS is based on the XOR operation, encryption combines the utilization of Chinese Remainder Theorem (CRT), SHA-256, and S-box for improved security. The same designed system is used for the generation of secret shares and the recovery of secret images. In addition, a sensitive system key is designed where three pairwise
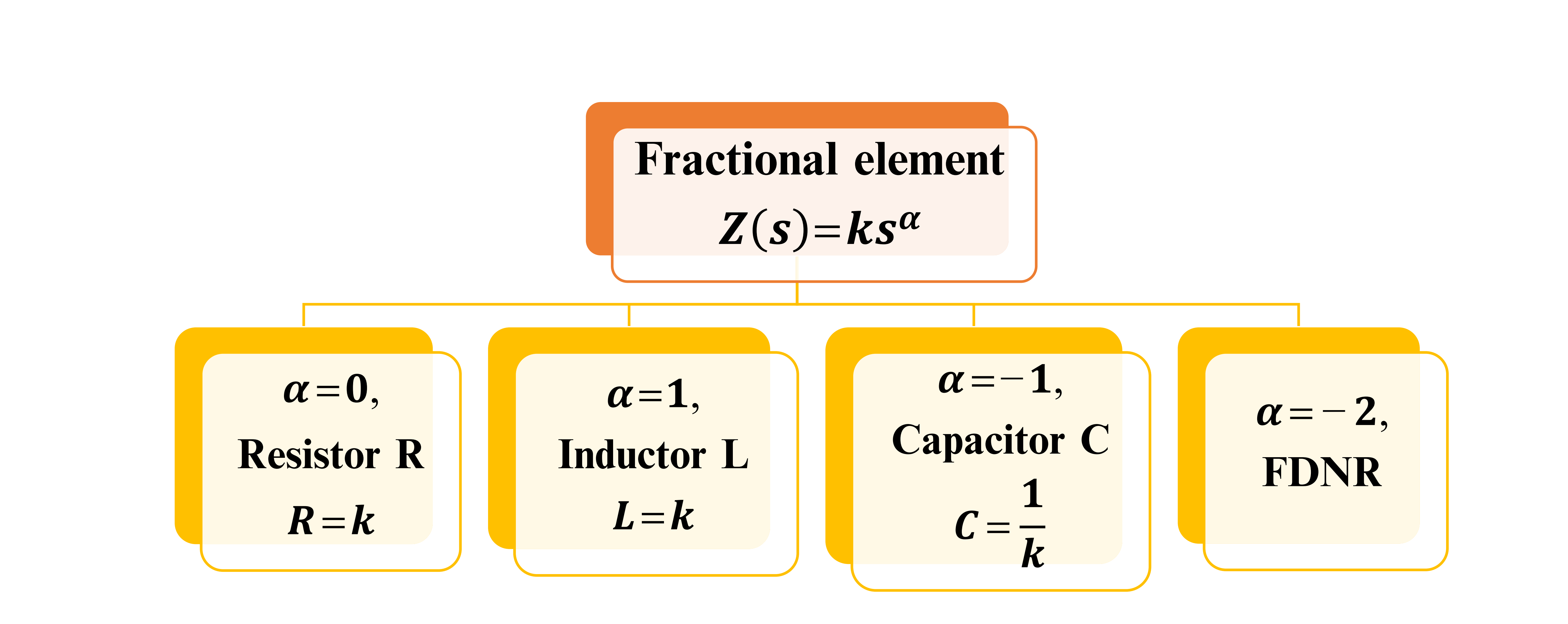
Fractional-Order Filter Design
One of the advantages of fractional order is the extra degree of freedom added by the fractional-order parameters, which enrich the analysis with more details in new dimensions. This chapter introduces factional-order conventional filters of orders α, 2α, and 3α. The general transfer functions of continuous-time filters (low-pass, high-pass, and band-pass filters) to the noninteger-order (fractional-order) domain are investigated. Also, mathematical expressions for the maximum and minimum frequencies, the half power frequencies, and the right-phase frequencies are derived. In addition, the
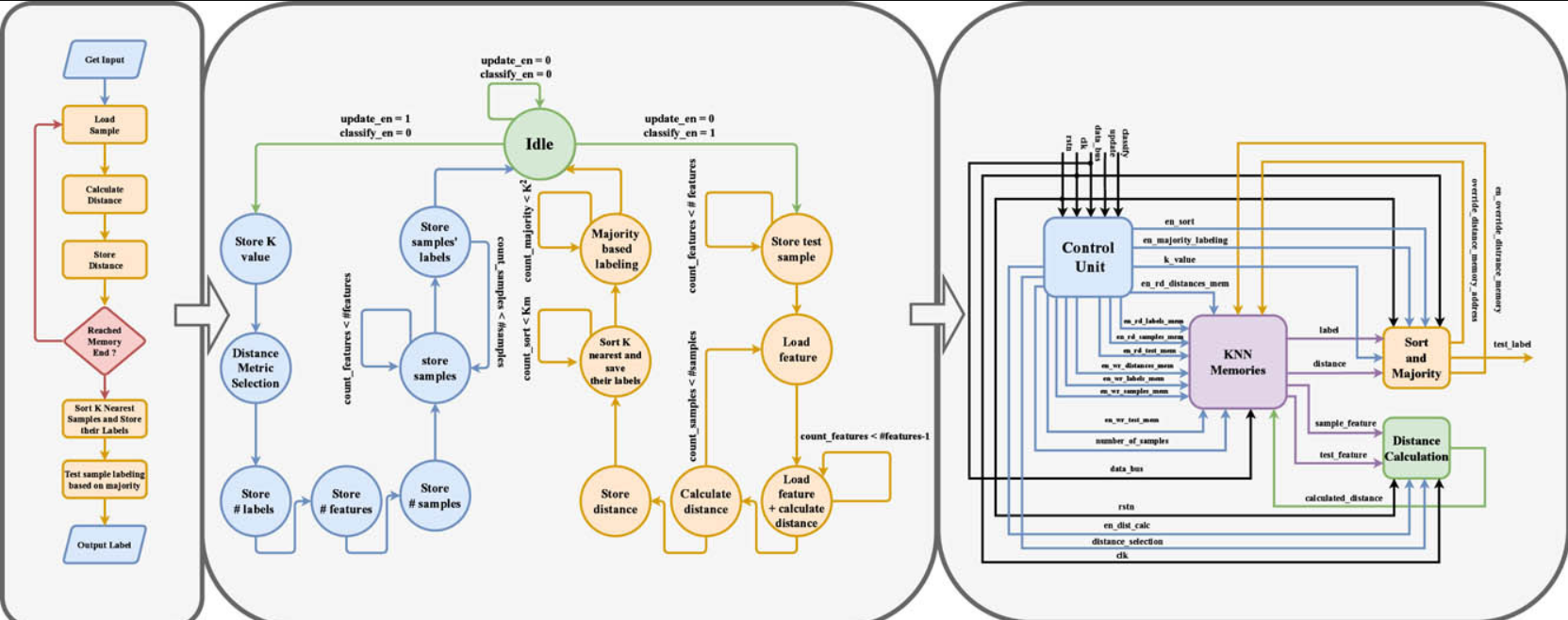
Reconfigurable hardware implementation of K-nearest neighbor algorithm on FPGA
Nowadays, Machine Learning is commonly integrated into most daily life applications in various fields. The K Nearest Neighbor (KNN), which is a robust Machine Learning algorithm, is traditionally used in classification tasks for its simplicity and training-less nature. Hardware accelerators such as FPGAs and ASICs are greatly needed to meet the increased requirements of performance for these applications. It is well known that ASICs are non-programmable and only fabricated once with high expenses, this makes the fabrication of a complete chip for a specific classification problem inefficient
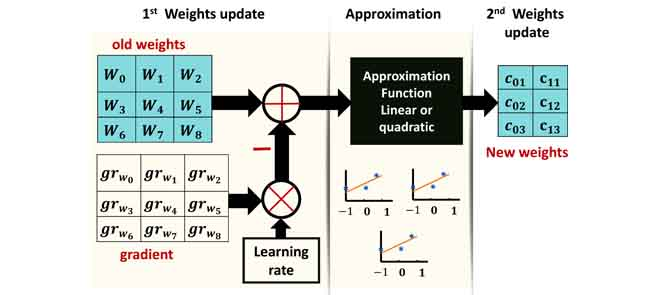
Deep Neural Networks-Based Weight Approximation and Computation Reuse for 2-D Image Classification
Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) are computationally and memory intensive, which present a big challenge for hardware, especially for resource-constrained devices such as Internet-of-Things (IoT) nodes. This paper introduces a new method to improve DNNs performance by fusing approximate computing with data reuse techniques for image recognition applications. First, starting from the pre-Trained network, then the DNNs weights are approximated based on the linear and quadratic approximation methods during the retraining phase to reduce the DNN model size and number of arithmetic operations. Then, the
Extended RC Impedance and Relaxation Models for Dissipative Electrochemical Capacitors
Electrochemical capacitors are a class of energy devices in which complex mechanisms of accumulation and dissipation of electric energy take place when connected to a charging or discharging power system. Reliably modeling their frequency-domain and time-domain behaviors is crucial for their proper design and integration in engineering applications, knowing that electrochemical capacitors in general exhibit anomalous tendency that cannot be adequately captured with the traditional RC-based models. In this study, we first review some of the widely used fractional-order models for the
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 10
- Next page ››
