Breadcrumb
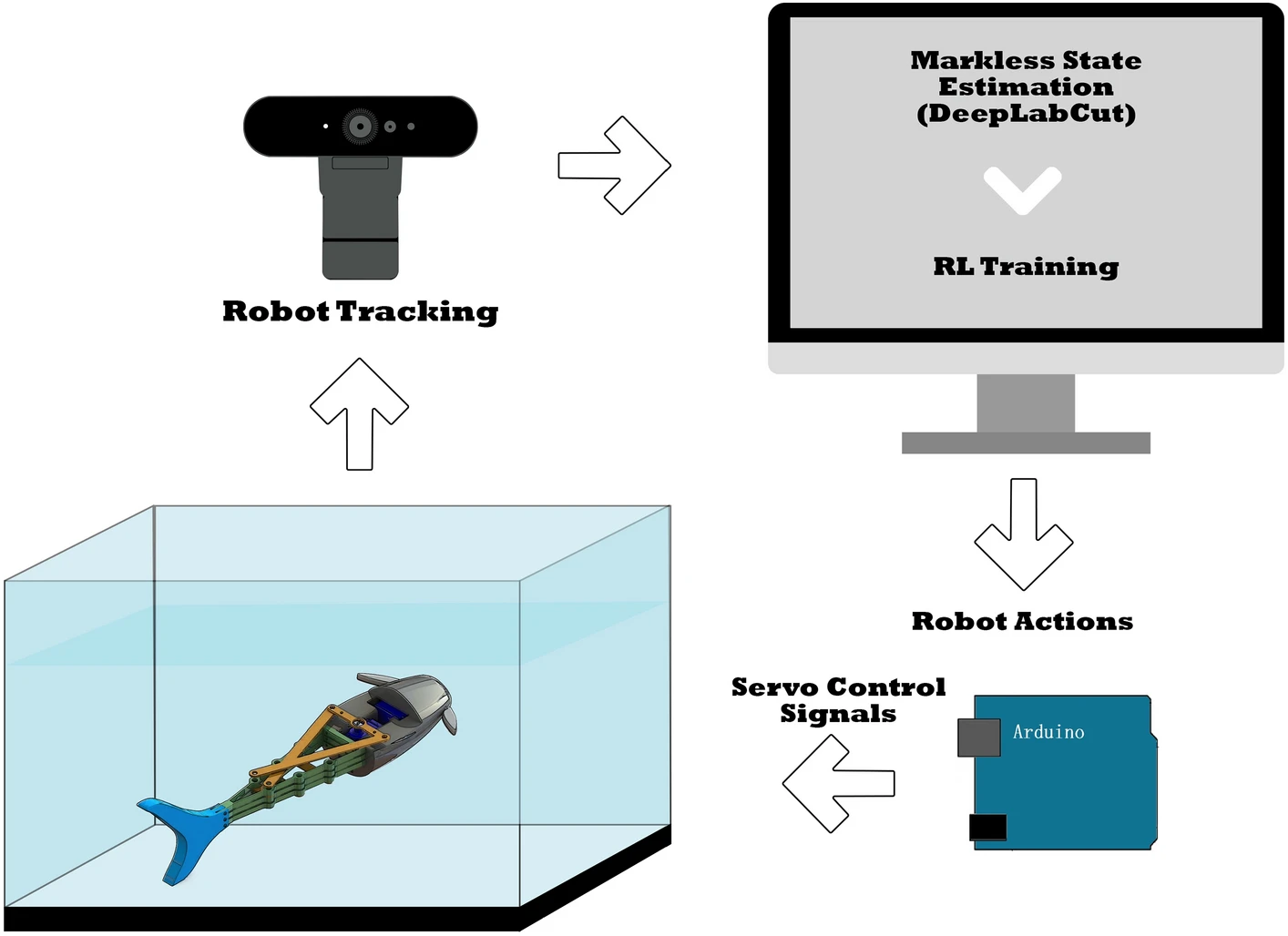
Design and control of soft biomimetic pangasius fish robot using fin ray effect and reinforcement learning
Soft robots provide a pathway to accurately mimic biological creatures and be integrated into their environment with minimal invasion or disruption to their ecosystem. These robots made from soft deforming materials possess structural properties and behaviors similar to the bodies and organs of living creatures. However, they are difficult to develop in terms of integrated actuation and sensing, accurate modeling, and precise control. This article presents a soft-rigid hybrid robotic fish inspired by the Pangasius fish. The robot employs a flexible fin ray tail structure driven by a servo
Quasi-Monte Carlo Technique With the Halton Sequence Applied To Mushroomwaveguide Photodetectors (WGPDs)
Monte Carlo (MC) simulation is a widely adopted computational method that relies on random sampling, but it is susceptible to exhibiting patterns and biases due to the use of pseudo-random numbers. In contrast, Quasi-Monte Carlo (QMC) techniques employ low discrepancy sequences, resulting in more evenly distributed random numbers and the potential for more accurate and reliable simulation outcomes. Mushroom-Waveguide Photodetectors (WGPDs) are integrated to a wide range of applications, and their performance is critically dependent on precise dimensional parameters. In this research, we
Guest Editorial: Fractional-Order Circuits and Systems: Theory, Design, and Applications
[No abstract available]
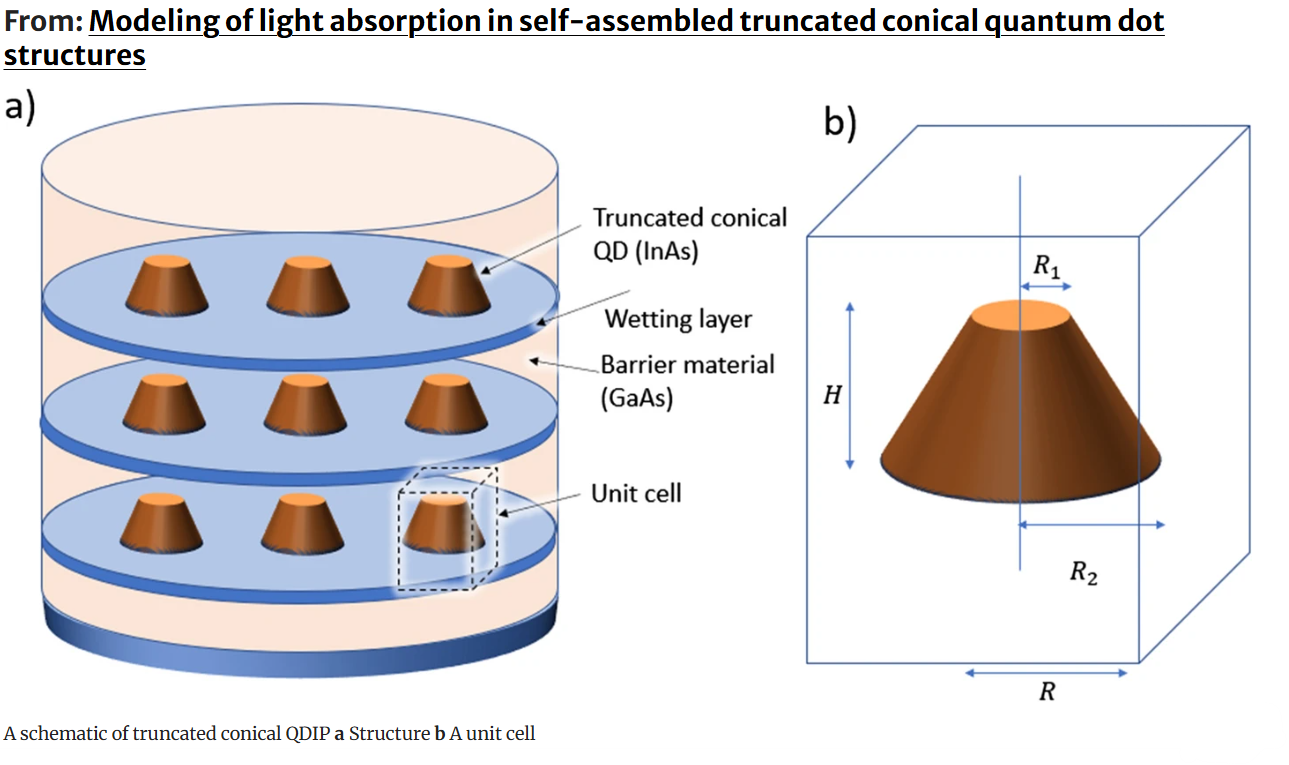
Modeling of light absorption in self-assembled truncated conical quantum dot structures
Quantum Dots have shown a significant potential as a top candidate for infrared photodetection at higher temperatures. In the presented work, a theoretical model for estimating the coefficient of optical absorption of self-assembled truncated conical quantum dot is developed. This model considers both bound-to-continuum and bound-to-bound absorption mechanisms that increase the accuracy of the absorption coefficient estimation. The developed model is based on estimating the bound states by diagonalizing the Hamiltonian matrix, where the density of states is computed using the Non-Equilibrium
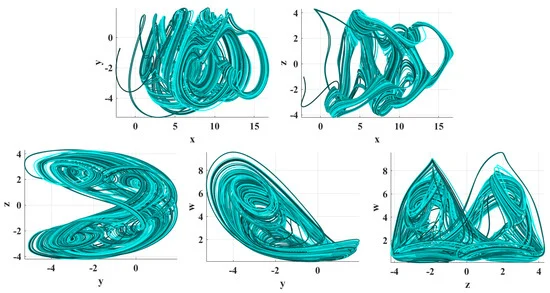
An Encryption Application and FPGA Realization of a Fractional Memristive Chaotic System
The work in this paper extends a memristive chaotic system with transcendental nonlinearities to the fractional-order domain. The extended system’s chaotic properties were validated through bifurcation analysis and spectral entropy. The presented system was employed in the substitution stage of an image encryption algorithm, including a generalized Arnold map for the permutation. The encryption scheme demonstrated its efficiency through statistical tests, key sensitivity analysis and resistance to brute force and differential attacks. The fractional-order memristive system includes a

Different Approximation Techniques For A FOPID Feedback Control of a DC Motor
DC motors are commonly employed in many industrial applications due to their various advantages. This study aims to compare the response of the Oustaloup-Recursive-Approximation (ORA) and El-Khazali's approximation method in controlling a DC motor with a FOPID controller. The two employed methods are used to design the FOPID and approximate. For various fractional orders, many behaviours are presented. A simulation comparison between these methods is performed regarding overshoot, settling time and rise time. © 2022 IEEE.
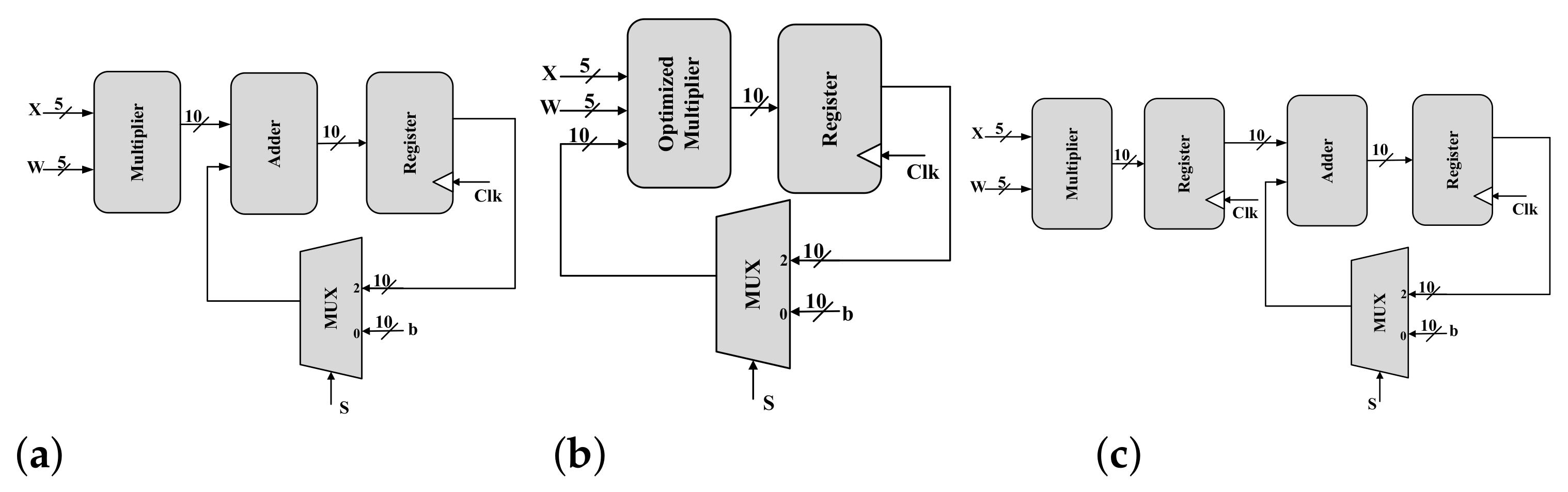
CNTFET-Based Ternary Multiply-and-Accumulate Unit
Multiply-Accumulate (MAC) is one of the most commonly used operations in modern computing systems due to its use in matrix multiplication, signal processing, and in new applications such as machine learning and deep neural networks. Ternary number system offers higher information processing within the same number of digits when compared to binary systems. In this paper, a MAC is proposed using a CNTFET-based ternary logic number. Specifically, we build a 5-trit multiplier and 10-trit adder as building blocks of two ternary MAC unit designs. The first is a basic MAC which has two methods to

Artificial Neural Network Chaotic PRNG and simple encryption on FPGA
Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) are remarkably able to fit complex functions, making them useful in various applications and systems. This paper uses ANN to fit the Pehlivan–Uyaroglu Chaotic System (PUCS) to produce an Artificial Neural Network Chaotic Pseudo-Random Number Generator (ANNC-PRNG). The proposed PRNG imitates the PUCS chaotic system's properties and attractor shape. The proposed ANNC-PRNG is implemented in a simple image encryption system on the Xilinx Kintex-7 Genesys 2 Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) board. Hardware realization of an ANN trained on chaotic time series has
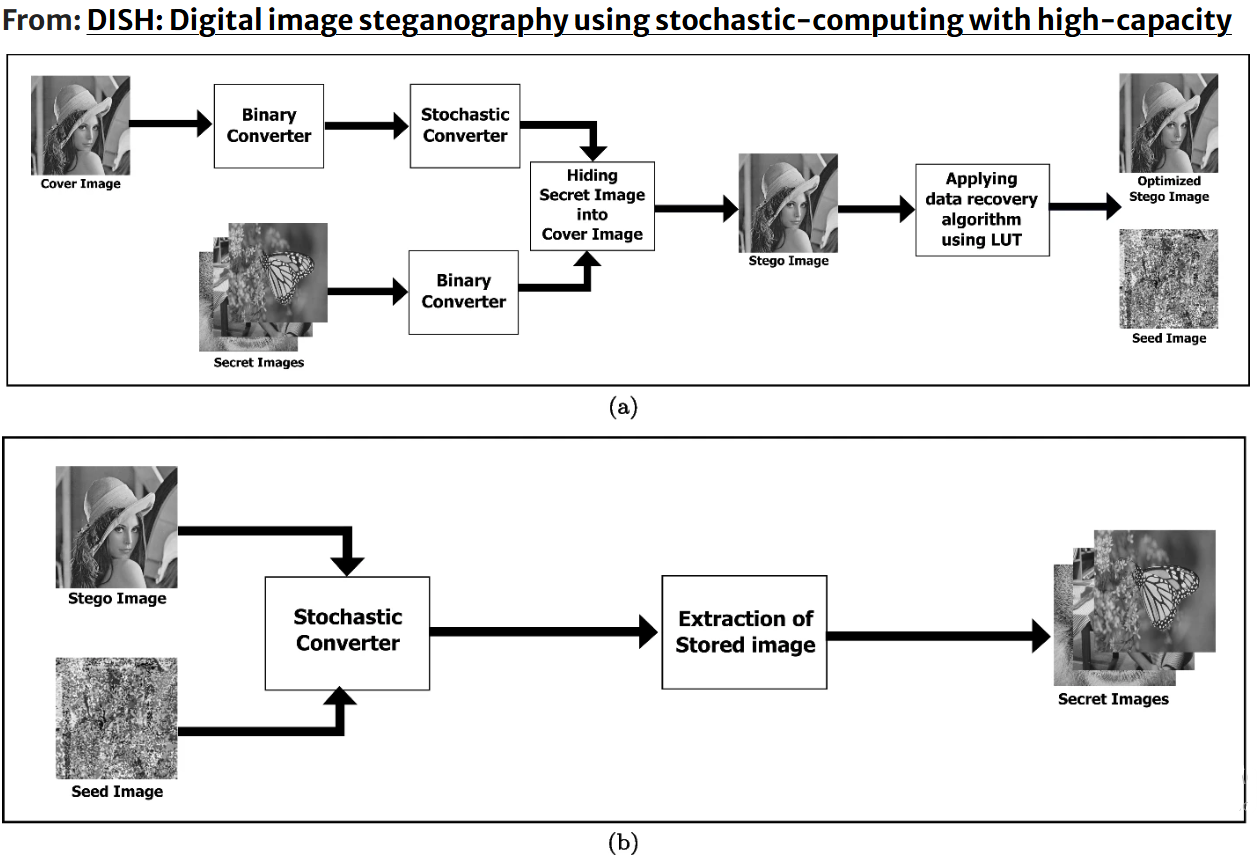
DISH: Digital image steganography using stochastic-computing with high-capacity
Stochastic computing is a relatively new approach to computing that has gained interest in recent years due to its potential for low-power and high-noise environments. It is a method of computing that uses probability to represent and manipulate data, therefore it has applications in areas such as signal processing, machine learning, and cryptography. Stochastic steganography involves hiding a message within a cover image using a statistical model. Unlike traditional steganography techniques that use deterministic algorithms to embed the message, stochastic steganography uses a probabilistic

Enhancing the Performance of Thin Film Photovoltaic Solar Cells using Truncated Conical Nanoparticles
Plasmonic photovoltaics are considered as promising photovoltaic candidate with enhanced optical absorption and quantum efficiency by embedding metallic nanoparticles in the photovoltaic active layer. In this paper, the efficiency enhancement of ultra-thin film solar cells with embedded truncated cone nanoparticles is studied. First, the natural electric field modes of the truncated cone in free-space are examined when excited by a plane wave. Parametric study is then performed to investigate the effects of the geometrical parameters of the structure on its resonant modes. Second, a uniform
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 7
- Next page ››
