Breadcrumb
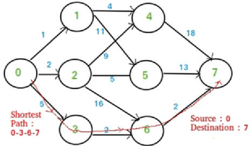
Comparison of Parallel and Serial Execution of Shortest Path Algorithms
Shortest Path Algorithms are an important set of algorithms in today's world. It has many applications like Traffic Consultation, Route Finding, and Network Design. It is essential for these applications to be fast and efficient as they mostly require real-Time execution. Sequential execution of shortest path algorithms for large graphs with many nodes is time-consuming. On the other hand, parallel execution can make these applications faster. In this paper, three popular shortest path algorithms-Dijkstra, Bellman-Ford, and Floyd Warshall-Are both implemented as serial and parallel programs

Fractional Order Systems: Optimization, Control, Circuit Realizations and Applications
Fractional Order Systems: Optimization, Control, Circuit Realizations and Applications consists of 21 contributed chapters by subject experts. Chapters offer practical solutions and novel methods for recent research problems in the multidisciplinary applications of fractional order systems, such as FPGA, circuits, memristors, control algorithms, photovoltaic systems, robot manipulators, oscillators, etc. This book is ideal for researchers working in the modeling and applications of both continuous-time and discrete-time dynamics and chaotic systems. Researchers from academia and industry who
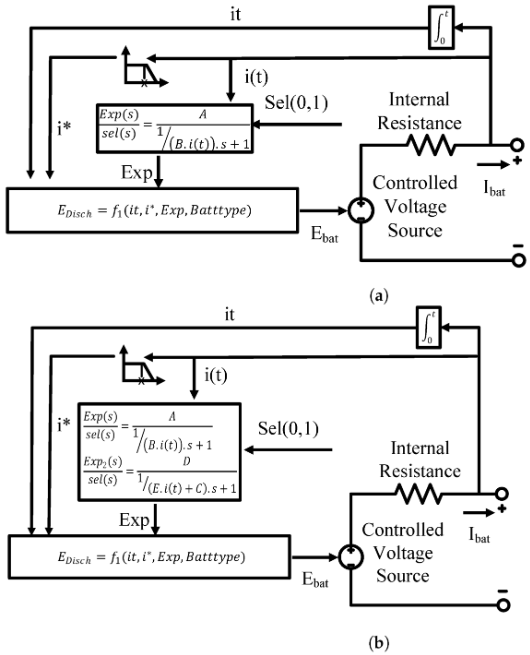
Parameter Identification of Li-ion Batteries: A Comparative Study
Lithium-ion batteries are crucial building stones in many applications. Therefore, modeling their behavior has become necessary in numerous fields, including heavyweight ones such as electric vehicles and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles, as well as lightweight ones like sensors and actuators. Generic models are in great demand for modeling the current change over time in real-time applications. This paper proposes seven dynamic models to simulate the behavior of lithium-ion batteries discharging. This was achieved using NASA room temperature random walk discharging datasets. The efficacy of
A generalized framework for elliptic curves based PRNG and its utilization in image encryption
In the last decade, Elliptic Curves (ECs) have shown their efficacy as a safe fundamental component in encryption systems, mainly when used in Pseudorandom Number Generator (PRNG) design. This paper proposes a framework for designing EC-based PRNG and maps recent PRNG design techniques into the framework, classifying them as iterative and non-iterative. Furthermore, a PRNG is designed based on the framework and verified using the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) statistical test suite. The PRNG is then utilized in an image encryption system where statistical measures
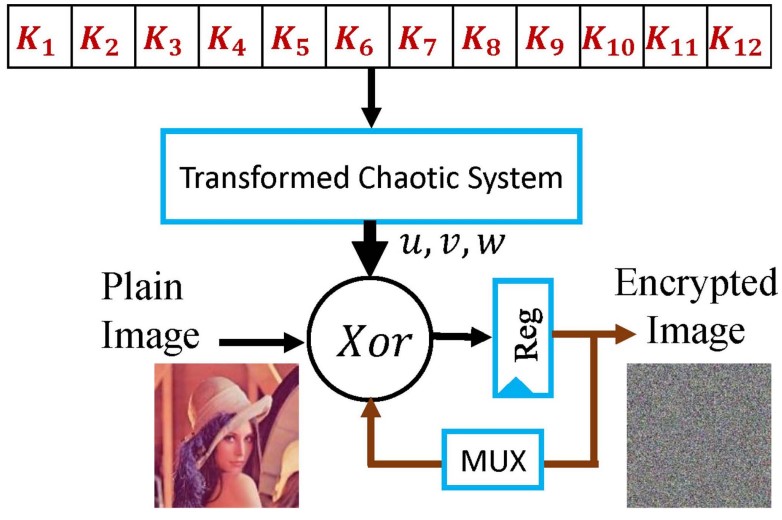
Self-Reproducing Hidden Attractors in Fractional-Order Chaotic Systems Using Affine Transformations
This article proposes a unified approach for hidden attractors control in fractional-order chaotic systems. Hidden attractors have small basins of attractions and are very sensitive to initial conditions and parameters. That is, they can be easily drifted from chaotic behavior into another type of dynamics, which is not suitable for encryption applications that require quite wide initial conditions and parameters ranges for encryption key design. Hence, a systematic coordinate affine transformation framework is utilized to construct transformed systems with self-reproducing attractors
On the generalization of fractional-order transmission lines
This paper demonstrates some fundamentals concerning the study of the Fractional order Transmission Line (FTL) operation. A numerical algorithm applied to study the transient analysis is shown describing the abnormal diffusion that appears in the operation of the TL. According to the steady state analysis of the FTL operation, the superior advantages over the conventional domain of imposing the fractional parameters are shown in this work. Moreover, all the conventional formulas are retrieved from the corresponding fractional ones by setting all fractional derivatives to unity. © 2014 IEEE.

Microstrip Coupled Line Bandpass Filter: A Stochastic Model
Coupled line microstrip filter is regarded to be a strong contender for high frequency and wireless applications, due to its compact size, inexpensive cost, and simple engineering manufacturing. The stochastic study of the proposed microstrip filter, based on the Monte Carlo Model, presented in this paper explores the uncertainties in the microstrip filter's design parameters and their influence on the filter's functionality. The filter's microstrip thickness, lengths, and spacing are all considered as design factors. The analysis investigates the variation of the standard deviations, the mean

IoT Microchip AVR Microcontroller's Fuses and Lock Bits High Voltage Programmer
This paper proposes a reliable wireless configuration bits programmer for remotely resetting incorrectly-written Microchip AVR microcontrollers' Fuses and Lock Bits. The incorrect configuration bits programming leads critically to a micro-controller malfunction which requires correct reprogramming. The proposed programmer utilizes Wi-Fi for enabling the remote configuration bits programming via a PC or a smart mobile device. It employs the Microchip AVR High Voltage Parallel and Serial Programming protocols which uniquely support the configuration bits programming feature. The configuration

Pseudo Random Number Generators Employing Three Numerical Solvers of Chaotic Generators
Pseudo-Random Number Generator (PRNG) is required for various applications, especially cryptography. PRNGs are employed in symmetric-key algorithms, where a single key is used as a seed to the PRNG to generate a sequence of random numbers that are employed to encrypt and decrypt certain data. This work proposes a PRN G system that employs the time series generated from the numerical solution of systems of chaotic-generators Differential Equations (DEs) utilizing three different DEs solvers; Euler, Runge-Kutta 4th order, and Runge-Kutta 5th order. Various systems were solved using each of the

Novel Edge AI with Power-Efficient Re-configurable LP-MAC Processing Elements
Deep learning has become increasingly important in various fields, such as robotics, image processing, and speech recognition. However, the high computational requirements of deep learning models make it challenging to deploy them on edge & embedded devices with constrained power and area budgets. This paper proposes a novel low-power technique for implementing deep learning models on edge devices called LP-MAC (Low Power Multiply Accumulate). LP-MAC is designed for fixed-point format operations and takes advantage of reusing the input vector for MAC operations. It provides a new hardware
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 6
- Next page ››
