Breadcrumb
MOS realizations of fractional-order elements
The exploitation of fractional calculus in engineering applications requires the utilization of fractional-order elements. As there is no immediate access to such type of elements, emulators that proportionally imitate their behavior are developed. The realization of emulators of fractional-order elements is based on the approximation of their impedance function. Subsequently, an advantageous option for the circuit implementation of the obtained, approximated impedance function is MOS transistor-based configurations, as they provide a dynamic system with electronically adjustable parameters
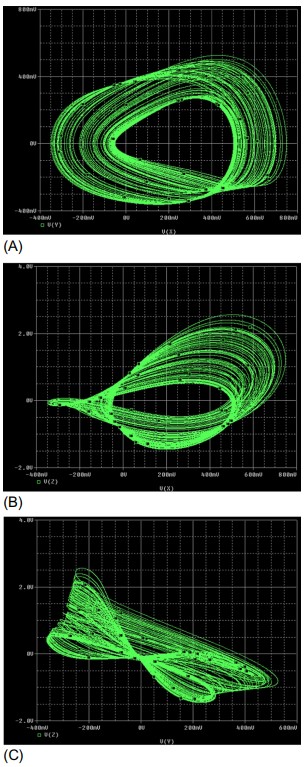
Dynamics, Circuit Design, Synchronization, and Fractional-Order Form of a No-Equilibrium Chaotic System
Systems without equilibrium such as electromechanical models with rotation and electrical circuits with cylindrical phase space were studied a long time ago. However, chaotic systems without equilibrium have received significant attention recently after the introduction of hidden attractors. Interestingly, an attractor of a no-equilibrium system is hidden because its basin of attraction does not intersect with any neighborhood of an unstable fixed point. This chapter presents a 3D no-equilibrium system with hidden chaotic attractors. The fundamental qualitative properties of the proposed no
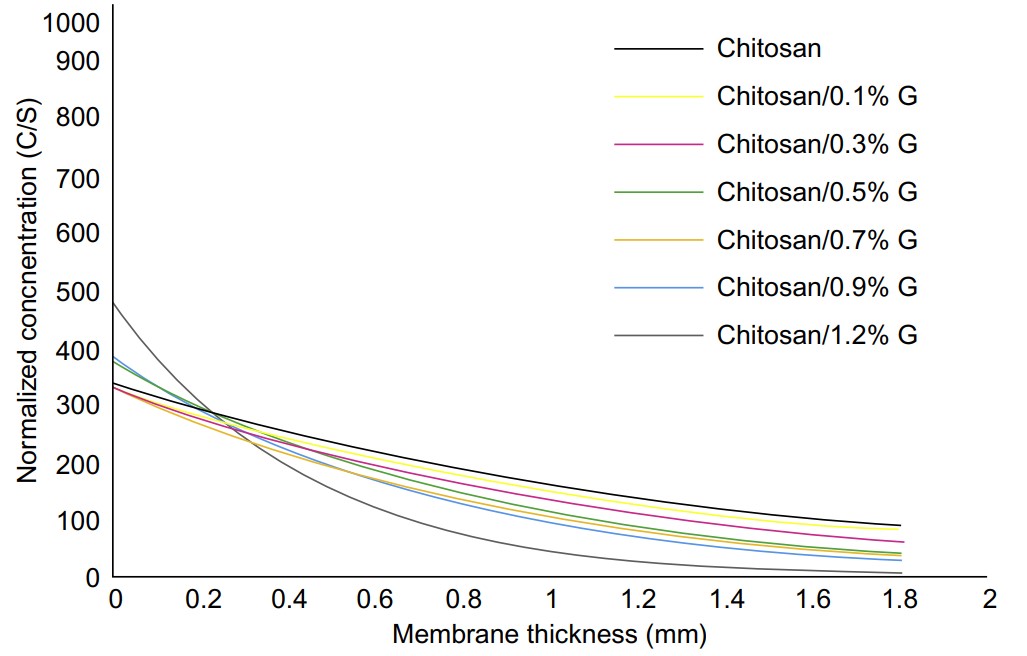
Design and fabrication of CNT/graphene-based polymer nanocomposite applications in nanosensors
Development and improvement of nanosensors have been active research areas over the last few decades. Many materials and compounds have been investigated for their sensing properties. This work is concerned with developing a new sensing layer for gas sensors based on chitosan as a polymer enhanced with graphene as a nanofiller. The graphene used for preparing the chitosan solution was at 0.1, 0.5, and 1 wt%. Many characterizations (such as using different pore size, gas permeability, mechanical properties, and electrical resistance) were tested to give full insight into the nanocomposite
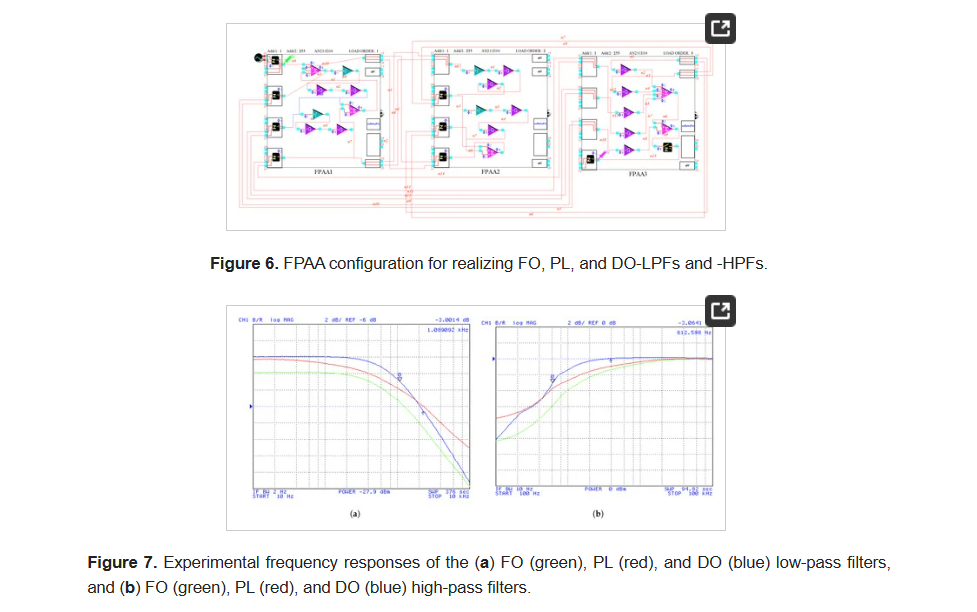
Field Programmable Analog Array Based Non-Integer Filter Designs
The approximation of the frequency behavior of fractional-order, power-law, and double-order filters can be performed by the same rational integer-order transfer function. This can be achieved through the utilization of a curve fitting based approximation. Moreover, their implementation can be performed by the same core, by only changing the corresponding time constants and scaling factors. The aforementioned findings are experimentally verified using a Field Programmable Analog Array device. © 2023 by the authors.

Observability of speed DC motor with self-tuning fuzzy-fractional-order controller
The DC motor is one of the simplest electrical machines used in industry since it is controlled by direct voltages and currents. These configurations have various advantages, allowing the machine to be adapted to the constraints of its specific application. The present chapter analyzes the DC motor with separate excitation without the use of a speed sensor to approximate the rotor speed. An analysis of the stability of the rotor speed estimation is performed. Enhanced control of the direct action is integrated into the adaptive observer to decrease the roundness capability of the model and
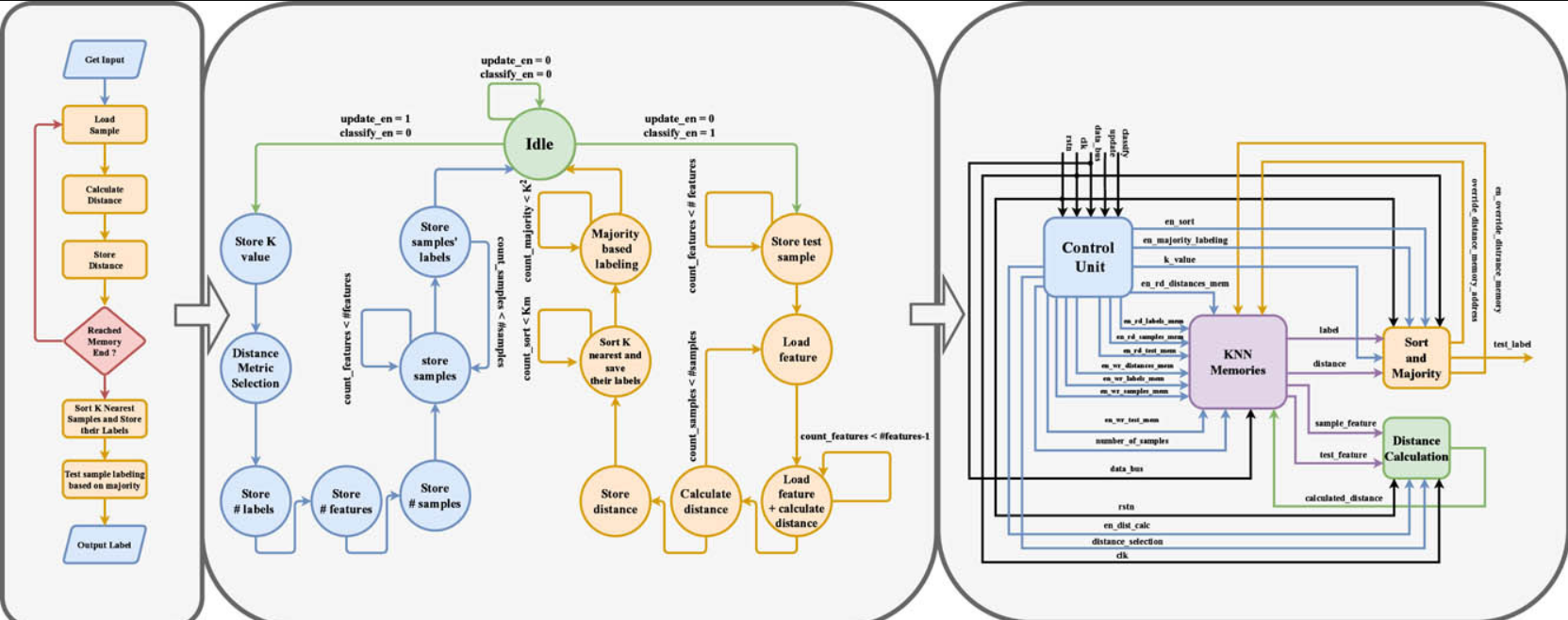
Reconfigurable hardware implementation of K-nearest neighbor algorithm on FPGA
Nowadays, Machine Learning is commonly integrated into most daily life applications in various fields. The K Nearest Neighbor (KNN), which is a robust Machine Learning algorithm, is traditionally used in classification tasks for its simplicity and training-less nature. Hardware accelerators such as FPGAs and ASICs are greatly needed to meet the increased requirements of performance for these applications. It is well known that ASICs are non-programmable and only fabricated once with high expenses, this makes the fabrication of a complete chip for a specific classification problem inefficient
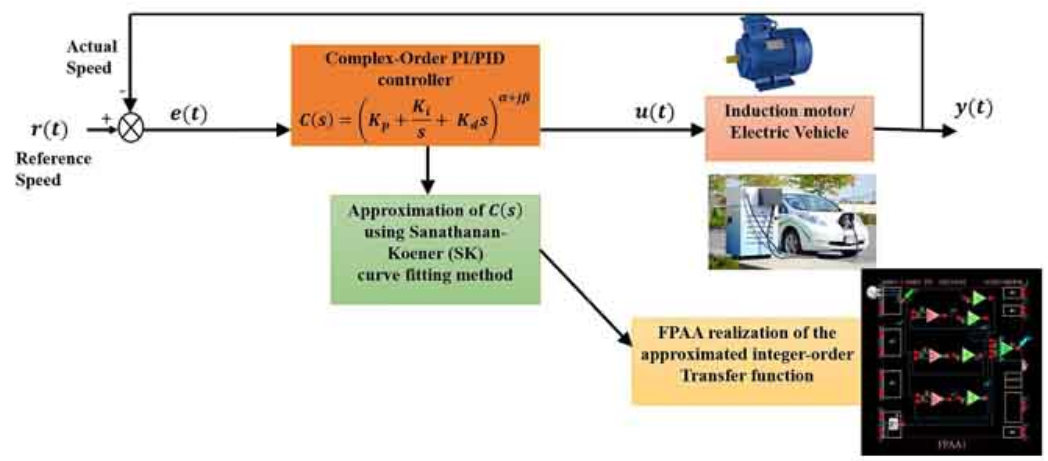
Design of Complex-Order PI/PID Speed Controllers and its FPAA Realization
Complex-order controllers are a generalized version of conventional integer-order controllers and are known to offer greater flexibility, better robustness, and improved system performance. This paper discusses the design of complex-order PI/PID controllers to control the speed of an induction motor drive and an electric vehicle. The speed-tracking performance of the complex-order controllers is compared with fractional-order controllers and conventional integer-order controllers. Implementing complex-order controllers is challenging due to commercial complex-order fractance element
Deep Learning Based Kinematic Modeling of 3-RRR Parallel Manipulator
This paper presents a novel low cost design for a 3-RRR Planar Parallel Manipulator (PPM). These manipulators proved their superiority over serial manipulators due to their speed, precision and smaller work space where the work space area is accounted for in the design to ensure that the robot is performing its task in a smooth and simple way without getting into any singularity points. The challenge with PPM is to obtain the kinematic constraint equations of the manipulator due to their complex non-linear behavior. Screw theory is a new approach that is used to compute the direct and inverse
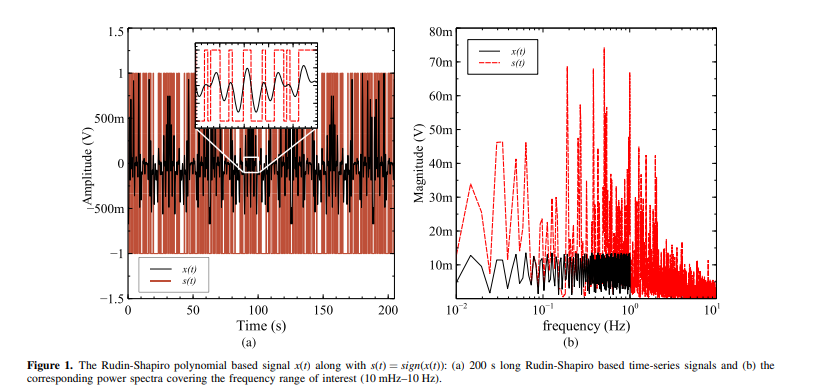
Electrical Impedance Spectroscopy Using a Wide-Band Signal Based on the Rudin-Shapiro Polynomials
Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) has become an increasingly important diagnostic and monitoring tool in many industries. An obstacle that arises when employing EIS in low and ultra low sub-Hz frequencies is the long measurement time associated with using the conventional frequency-sweep method. One possible solution to this problem is to use wide-band signals that cover at once the entire frequency range of interest. In this work, we explore and validate the use of such a signal obtained from the Rudin-Shapiro polynomial over the frequency range 10 mHz to 10 Hz. The proposed signal

A collection of interdisciplinary applications of fractional-order circuits
An attractive feature of fractional calculus is its application in various interdisciplinary fields, extending from biomedical and biological notions to mechanical properties. For their description, fractional-order models have outperformed the corresponding integer-order models, resulting in a more realistic behavior, due to the additional degrees of freedom offered and the long-term memory effect that reflects the fractional order. These improved features are processed by appropriate circuit implementations, derived through several approximation methods, whose primary objective is to provide
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 7
- Next page ››
