Breadcrumb
Fractional-order and memristive nonlinear systems: Advances and applications
[No abstract available]

High Gain Meander Line Antenna for 2.4 GHz Bluetooth Applications
In this paper, a highly directive meander line antenna is proposed to be utilized in the unlicensed Bluetooth band. The main goal of the proposed structure is to achieve low profile, and high gain in the Bluetooth band. Moreover, the antenna should be of low cost to be suitable for commercial use. The proposed structure is simulated using HFSS and CST to verify the obtained results. The maximum calculated gain of the antenna is 9.95 dBi (9.79 dBi) along the end-fire direction as simulated by HFSS (CST). The antenna demonstrated high radiation efficiency which is around 96% over its working
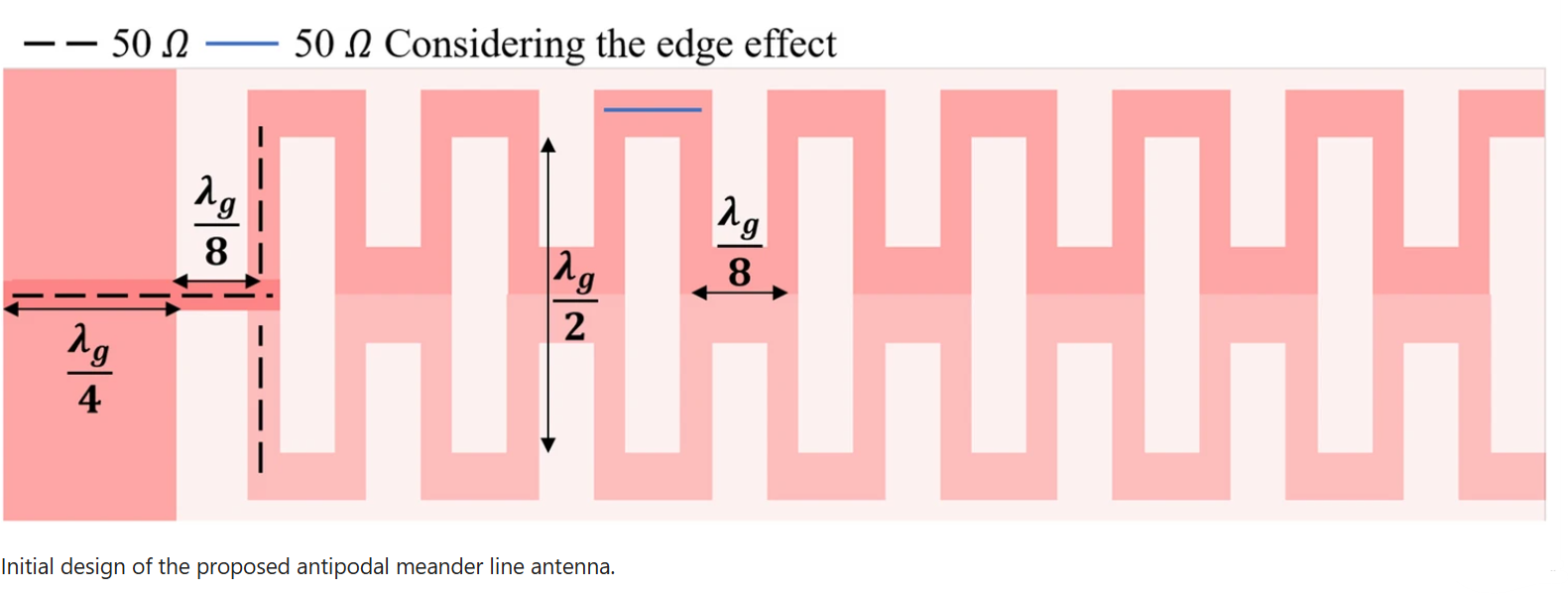
High gain antipodal meander line antenna for point-to-point WLAN/WiMAX applications
This paper introduces a planar antipodal meander line antenna fabricated using RO3003 substrate. The proposed antenna is designed to radiate in the end-fire direction, achieving a maximum measured gain of 10.43 dBi within its working bandwidth, which ranges from 2.24 GHz to 2.7 GHz, covering long-range WLAN/WiMAX applications. A systematic procedure is adopted in the design process to prove its tunability to cover other application requirements in terms of gain and bandwidth. The proposed design steps show that the bandwidth and the gain can independently be controlled by adjusting specific

Battery Modeling with Mittag-Leffler Function
In various areas of life, rechargeable lithium-ion batteries are the technology of choice. Equivalent circuit models are utilized extensively in characterizing and modeling energy storage systems. In real-time applications, several generic-based battery models are created to simulate the battery's charging and discharging behavior more accurately. In this work, we present two generic battery models based on Mittag-Leffler function using a generic Standard battery model as a reference. These models are intended to fit the continuous discharging cycles of lithium-ion, Nickel-cadmium, and Nickel
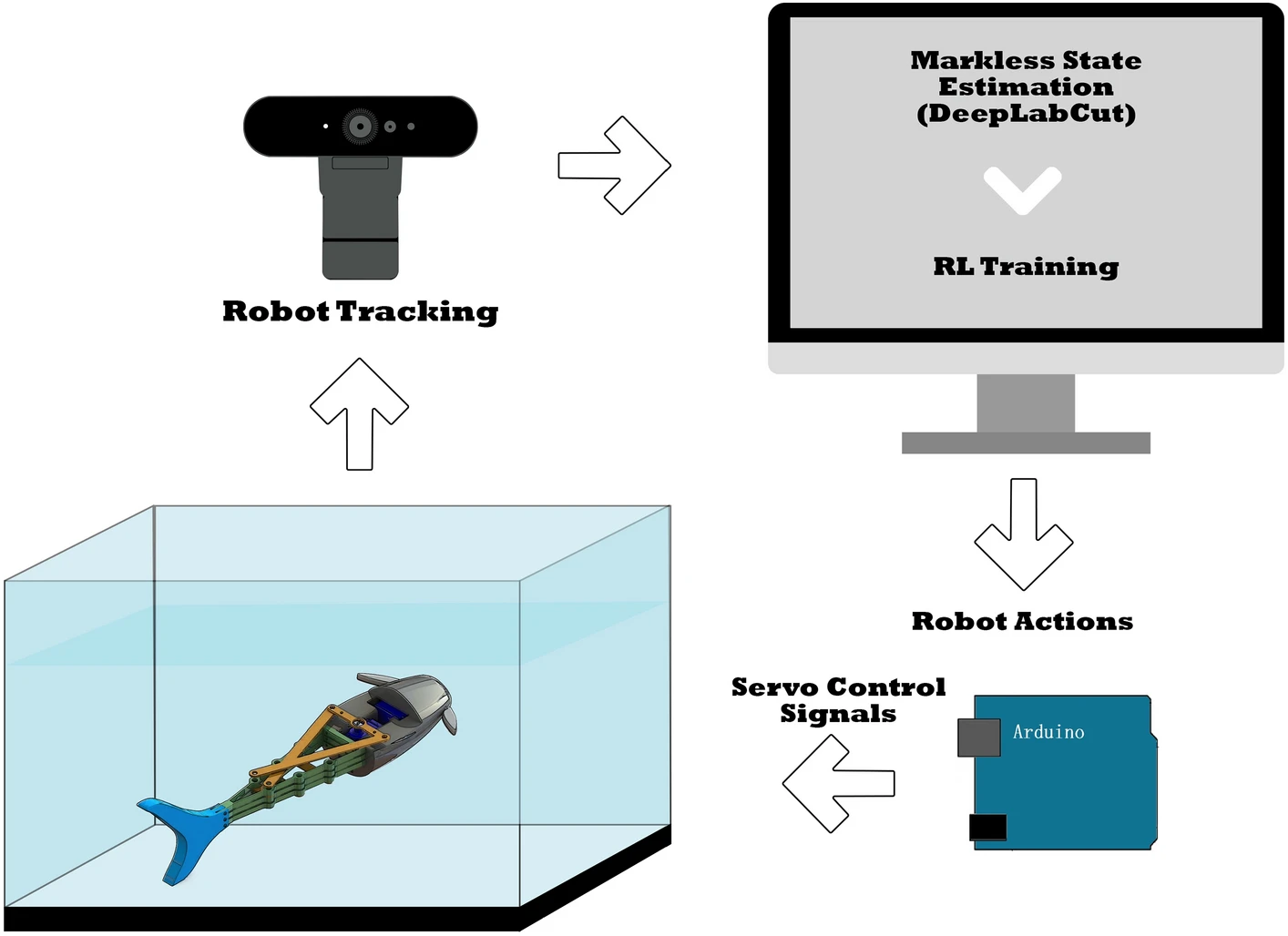
Design and control of soft biomimetic pangasius fish robot using fin ray effect and reinforcement learning
Soft robots provide a pathway to accurately mimic biological creatures and be integrated into their environment with minimal invasion or disruption to their ecosystem. These robots made from soft deforming materials possess structural properties and behaviors similar to the bodies and organs of living creatures. However, they are difficult to develop in terms of integrated actuation and sensing, accurate modeling, and precise control. This article presents a soft-rigid hybrid robotic fish inspired by the Pangasius fish. The robot employs a flexible fin ray tail structure driven by a servo
Quasi-Monte Carlo Technique With the Halton Sequence Applied To Mushroomwaveguide Photodetectors (WGPDs)
Monte Carlo (MC) simulation is a widely adopted computational method that relies on random sampling, but it is susceptible to exhibiting patterns and biases due to the use of pseudo-random numbers. In contrast, Quasi-Monte Carlo (QMC) techniques employ low discrepancy sequences, resulting in more evenly distributed random numbers and the potential for more accurate and reliable simulation outcomes. Mushroom-Waveguide Photodetectors (WGPDs) are integrated to a wide range of applications, and their performance is critically dependent on precise dimensional parameters. In this research, we
Guest Editorial: Fractional-Order Circuits and Systems: Theory, Design, and Applications
[No abstract available]

Hardware Realization of High-Speed Area-Efficient Floating Point Arithmetic Unit on FPGA
Floating point representations are required in many applications due to their universality and ability to represent huge numbers accurately and in compact bit-width. Floating point arithmetic is complex, performance inefficient, and area-consuming compared to integer arithmetic operations. In this paper, hardware realization of area-efficient high-performance floating point arithmetic units for IEEE 754 floating point single precision and double precision formats on FPGA are proposed. The proposed units achieved the same accuracy as software in all tested cases and were able to produce the
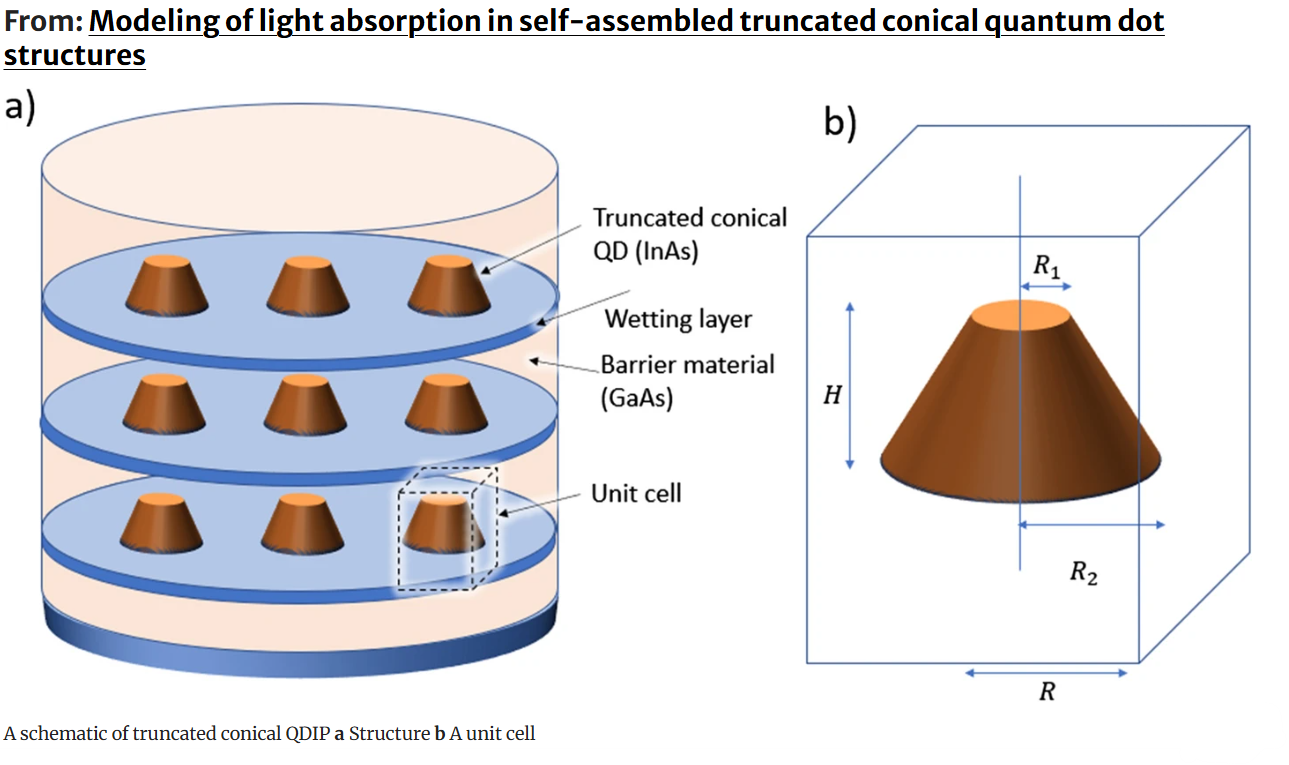
Modeling of light absorption in self-assembled truncated conical quantum dot structures
Quantum Dots have shown a significant potential as a top candidate for infrared photodetection at higher temperatures. In the presented work, a theoretical model for estimating the coefficient of optical absorption of self-assembled truncated conical quantum dot is developed. This model considers both bound-to-continuum and bound-to-bound absorption mechanisms that increase the accuracy of the absorption coefficient estimation. The developed model is based on estimating the bound states by diagonalizing the Hamiltonian matrix, where the density of states is computed using the Non-Equilibrium
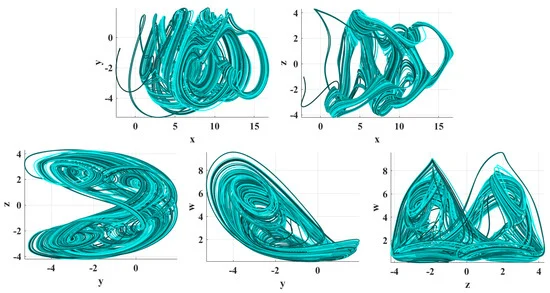
An Encryption Application and FPGA Realization of a Fractional Memristive Chaotic System
The work in this paper extends a memristive chaotic system with transcendental nonlinearities to the fractional-order domain. The extended system’s chaotic properties were validated through bifurcation analysis and spectral entropy. The presented system was employed in the substitution stage of an image encryption algorithm, including a generalized Arnold map for the permutation. The encryption scheme demonstrated its efficiency through statistical tests, key sensitivity analysis and resistance to brute force and differential attacks. The fractional-order memristive system includes a
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 8
- Next page ››
