Breadcrumb
Realistic Wireless Smart-Meter Network Optimization Using Composite RPL Metric
In smart metering applications, transferring and collecting data within delay constraints is crucial. IoT devices are usually resource-constrained and need reliable and energy-efficient routing protocol. Furthermore, meters deployed in lossy networks often lead to packet loss and congestion. In smart grid communication, low latency and low energy consumption are usually the main system targets. Considering these constraints, we propose an enhancement in RPL to ensure link reliability as well as low latency. We refer to the proposed new additive composite metric as Delay-Aware RPL (DA-RPL)

Adsorption as an Emerging Technology and Its New Advances of Eco-Friendly Characteristics: Isotherm, Kinetic, and Thermodynamic Analysis
Water contamination with paints causes a colour agent to the water that negatively affects the environment, organisms, and humans. Different physicochemical processes are applied for wastewater treatment; however, they have many drawbacks such as high cost, generating toxic waste, and non-effective at low concentrations. Adsorption is considered a promising technique for pollutant removal from polluted wastewater. Commercial activated carbon, nano-materials, and natural biological materials are used as adsorbents in adsorption. This chapter focuses on discussing the adsorption process, the

Sustainable Energy-Aware Task Scheduling for Wearable Medical Device Using Flower Pollination Algorithm
Power management and energy conservation are crucial for medical wearable devices that rely on energy harvesting. These devices operate under strict power budgets and require prolonged and stable operation. To achieve this, Energy-aware task scheduling is proposed as a solution to minimize energy consumption while ensuring the continued operational capabilities of the device. our paper presents a task scheduling method using the Flower Pollination Algorithm (FPA). The proposed task scheduling focuses on managing the activity of key components such as the heart rate sensor, temperature sensor
An Efficient DMO Task Scheduling Technique for Wearable Biomedical Devices
The popularity of wearable devices has grown as they improve the quality of life in many applications. In particular, for medical devices, energy harvesters are the dominating source of energy for wearable devices. However, their power budget is limited. Thus, power-saving techniques are essential components in the whole technology stack of those devices. That is, choosing the optimal schedule for different tasks running on the wearable device can help to reduce energy consumption. This paper presents a sensor task scheduling technique for optimizing energy consumption for energy harvesting

Preparation and Characterization of nZVI, Bimetallic Fe 0-Cu, and Fava Bean Activated Carbon-Supported Bimetallic AC-F e 0-Cu for Anionic Methyl Orange Dye Removal
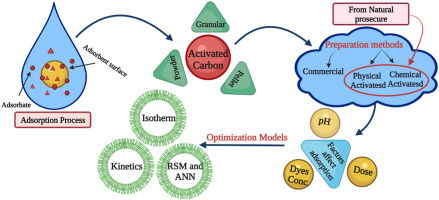
Review of activated carbon adsorbent material for textile dyes removal: Preparation, and modelling
Water contamination with colours and heavy metals from textile effluents has harmed the ecology and food chain, with mutagenic and carcinogenic effects on human health. As a result, removing these harmful chemicals is critical for the environment and human health. Various standard physicochemical and biological treatment technologies are used; however, there are still some difficulties. Adsorption is described as a highly successful technology for removing contaminants from textile-effluents wastewater compared to other methods. Several adsorbent materials, including nanomaterials, natural
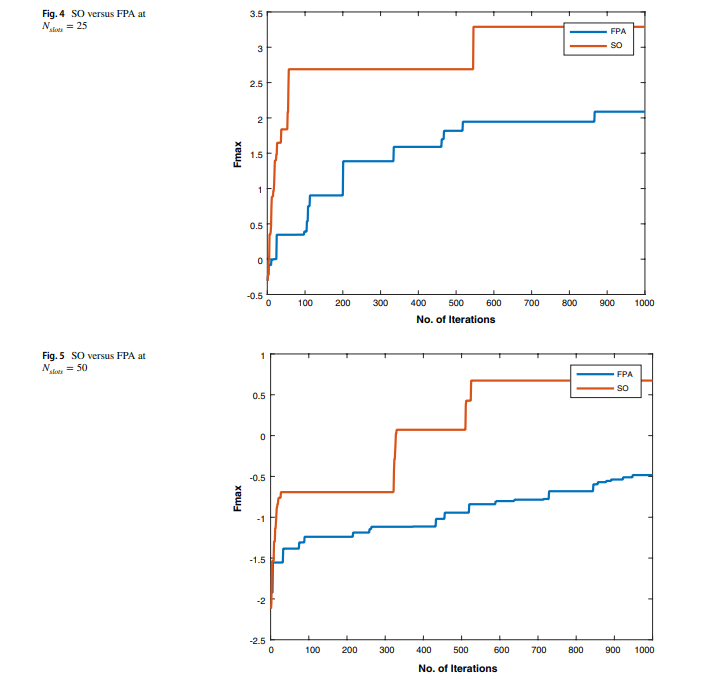
A power-aware task scheduler for energy harvesting-based wearable biomedical systems using snake optimizer
There is an increasing interest in energy harvesting for wearable biomedical devices. This requires power conservation and management to ensure long-term and steady operation. Hence, task scheduling algorithms will be used throughout this work to provide a reliable solution to minimize energy consumption while considering the system operation constraints. This study proposes a novel power-aware task scheduler to manage system operations. For example, we used the scheduler to handle system operations, including heart rate and temperature sensors. Two optimization techniques have been used to
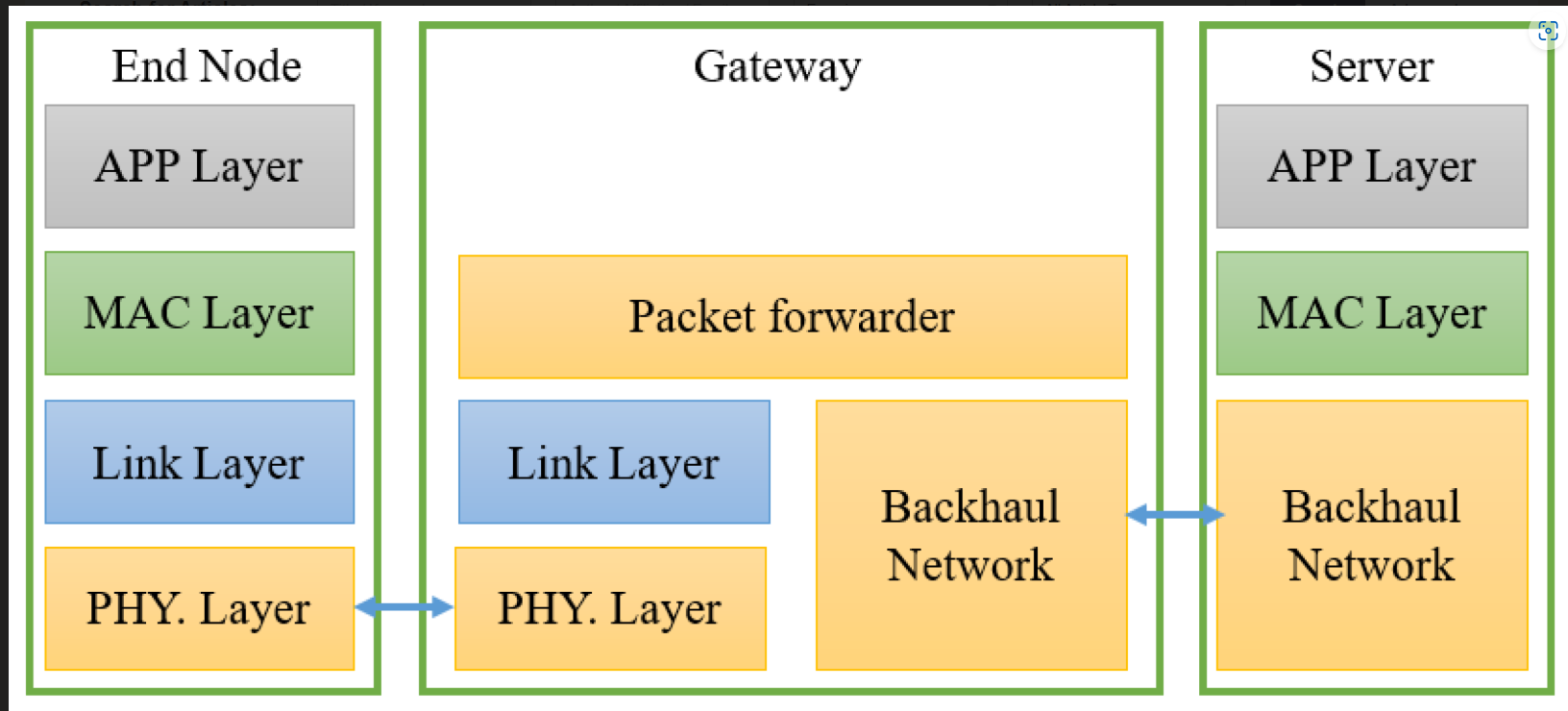
Internet of Things: A Comprehensive Overview on Protocols, Architectures, Technologies, Simulation Tools, and Future Directions
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a global network of interconnected computing, sensing, and networking devices that can exchange data and information via various network protocols. It can connect numerous smart devices thanks to recent advances in wired, wireless, and hybrid technologies. Lightweight IoT protocols can compensate for IoT devices with restricted hardware characteristics in terms of storage, Central Processing Unit (CPU), energy, etc. Hence, it is critical to identify the optimal communication protocol for system architects. This necessitates an evaluation of next-generation

Implementation of Multi-Step Bias-Flip Rectifier for Piezoelectric Energy Harvesting
The full-wave rectifier is an essential step for extracting energy from a piezoelectric source. Yet, the inherent capacitance of the piezoelement significantly is considered a limitation of the efficiency of extraction. To address this issue, the bias-flip rectifier can be used. However, this rectifier needs large inductor and precise tuning. The large inductor increases the overall volume of the system which is inefficient. This paper address the problems with the traditional bias-flip rectifier by introducing an enhanced multi-step bias-flip rectifier to achieve a high voltage-flip
Accelerated Edge Detection Algorithm for High-Speed Applications
Digital Image Processing (DIP) is a growing field for various applications, such as autonomous vehicles and video surveillance. To improve the performance of DIP systems, image processing algorithms are implemented in hardware rather than software. The idea here is primarily to get a faster system than software imaging or other alternative hardware. Field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs) have the advantages of parallel processing, low cost, and low power consumption. These semiconductor devices contain many logic blocks that can be programmed to perform everything from basic digital gate-level
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 2
- Next page ››
