Breadcrumb

In-Memory Associative Processors: Tutorial, Potential, and Challenges
In-memory computing is an emerging computing paradigm that overcomes the limitations of exiting Von-Neumann computing architectures such as the memory-wall bottleneck. In such paradigm, the computations are performed directly on the data stored in the memory, which highly reduces the memory-processor communications during computation. Hence, significant speedup and energy savings could be achieved especially with data-intensive applications. Associative processors (APs) were proposed in the seventies and recently were revived thanks to the high-density memories. In this tutorial brief, we
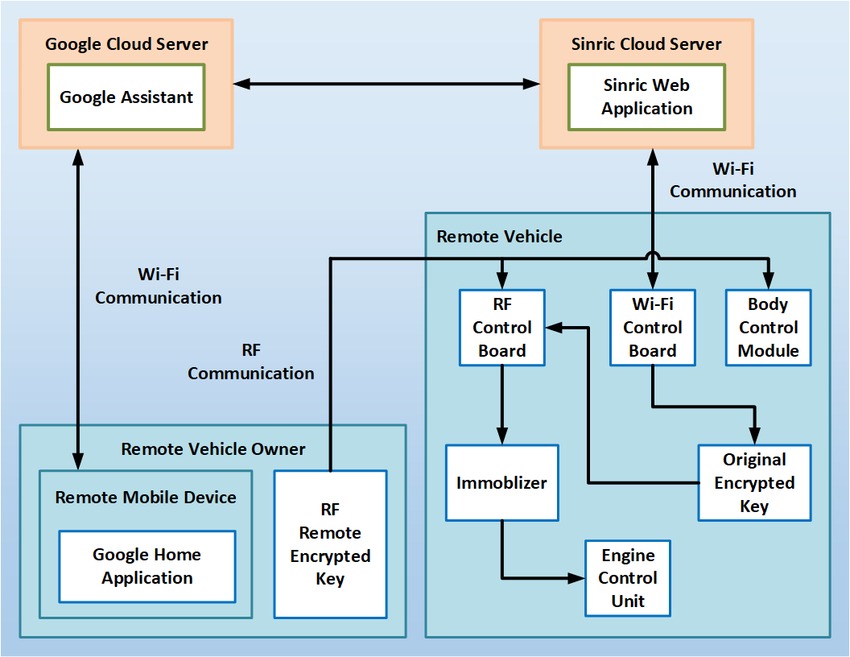
A Reliable Secure Architecture for Remote Wireless Controlling of Vehicle's Internal Systems based on Internet of Vehicles using RF and Wi-Fi
Internet of Vehicles is considered one of the most unprecedented outputs of the Internet of Things. No one has realized or even expected the rapidly-growing revolution regarding autonomous connected vehicles. Nowadays, Internet of Vehicles is massively progressing from Vehicular Ad-Hoc Networks as a huge futuristic research and development discipline. This paper proposes a novel reliable and secure architecture for ubiquitously controlling remote connected cars' internal systems, such as engine, doors' locks, sunroof, horn, windows' and lights' control systems. The main contribution is that
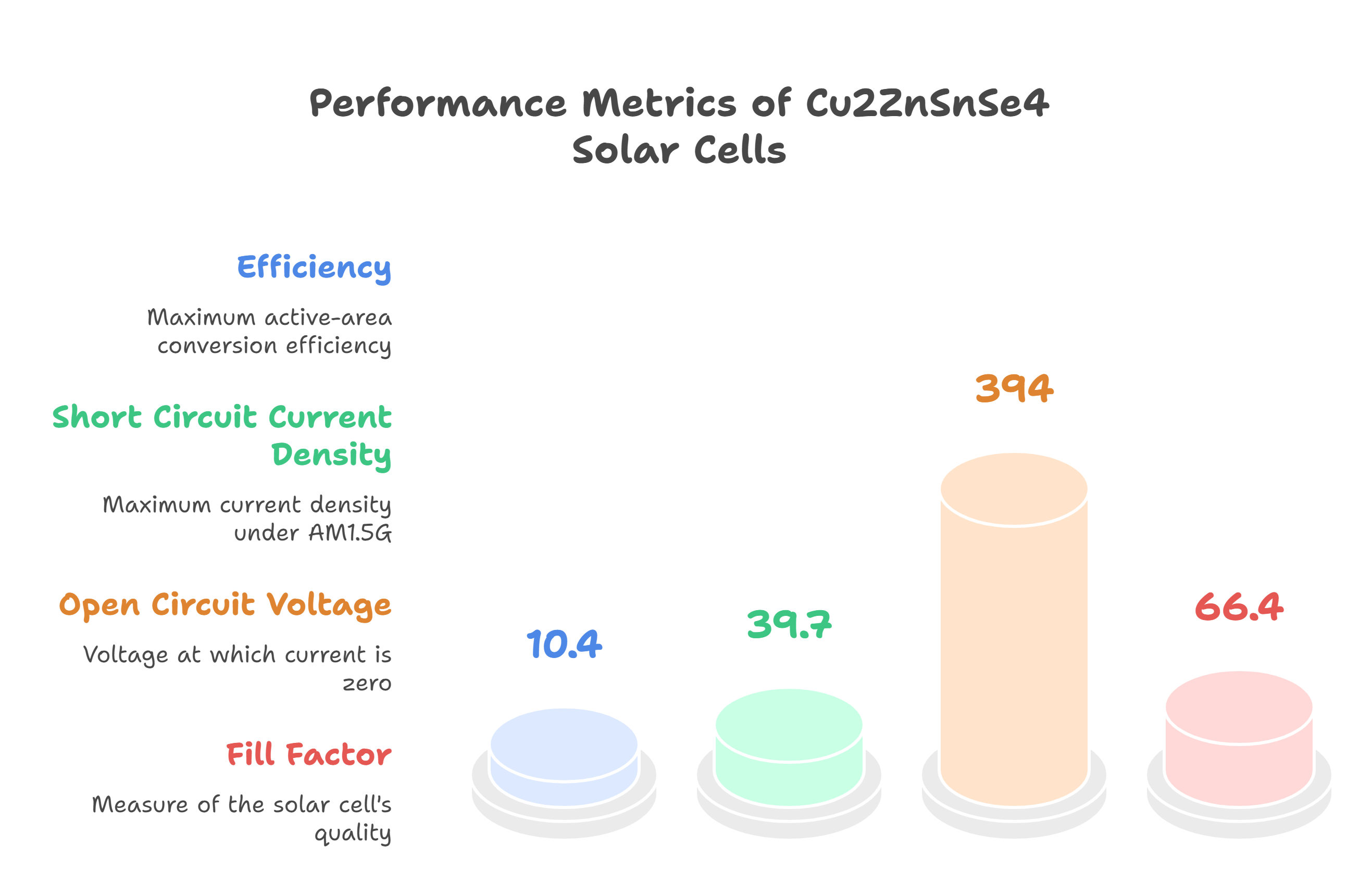
Physical and electrical characterization of high-performance Cu2ZnSnSe4based thin film solar cells
We report on the electrical, optical and physical properties of Cu2ZnSnSe4solar cells using an absorber layer fabricated by selenization of sputtered Cu, Zn and Cu10Sn90multilayers. A maximum active-area conversion efficiency of 10.4% under AM1.5G was measured with a maximum short circuit current density of 39.7 mA/cm2, an open circuit voltage of 394 mV and a fill factor of 66.4%. We perform electrical and optical characterization using photoluminescence spectroscopy, external quantum efficiency, current-voltage and admittance versus temperature measurements in order to derive information
Bio-inspired adsorption sheets from waste material for anionic methyl orange dye removal
Abstract: Nano zero-valent iron (nZVI), bimetallic nano zero-valent iron-copper (Fe0–Cu), and Raw algae (sargassum dentifolium) activated carbon-supported bimetallic nano zero-valent iron-copper (AC-Fe0–Cu) are synthesized and characterized using FT-IR, XRD, and SEM. The maximum removal capacity is demonstrated by bimetallic activated carbon AC-Fe0–Cu, which is estimated at 946.5 mg/g capacity at the condition pH = 7, 30 min contact time under shaking at 120 rpm at ambient temperature, 200 ppm of M.O, and 1 g/l dose of raw algae-Fe0–Cu adsorbent. The elimination capability of the H3PO4
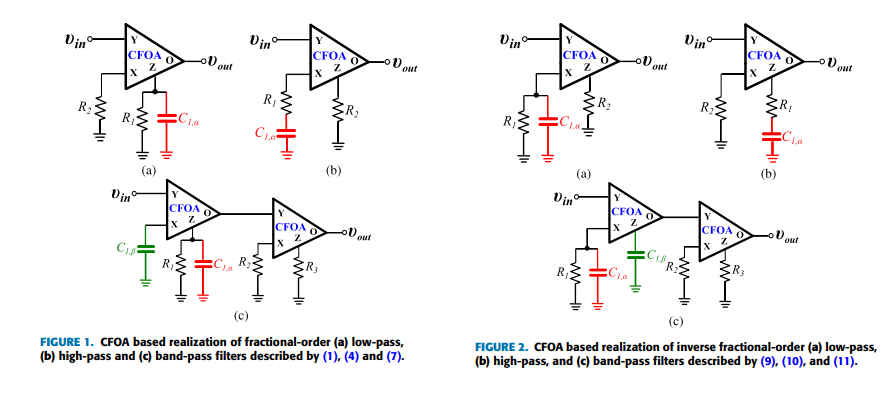
Non-Integer Order Generalized Filters Designs
Non-integer order filters can be derived from a generalized structure presented in this work. More specifically, fractional-order and power-law filters of single- or double-order are special cases of non-integer order filters with three degrees of freedom and can be implemented using a Current Feedback Operational Amplifier as the active element. The transfer function is formed as a ratio of two impedances which can be synthesized using Foster or Cauer RC networks. A curve-fitting based technique is employed for approximating the magnitude and phase of each impedance. The behavior of the
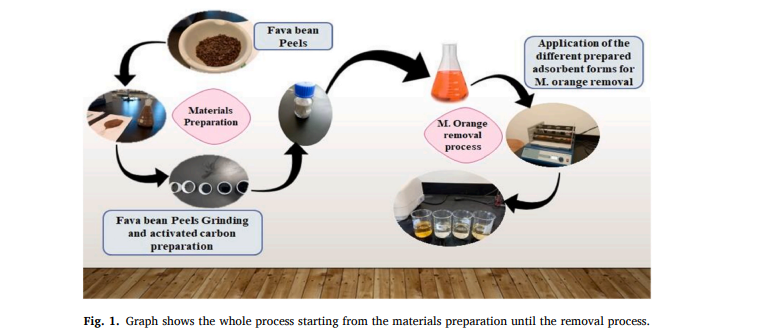
Experimental investigation of methyl-orange removal using eco-friendly cost-effective materials raw fava bean peels and their formulated physical, and chemically activated carbon
The discharge of effluents from dye industries into water streams poses a significant environmental and public health risk. In response, eco-friendly adsorbents derived from agricultural waste, such as Fava Bean Peels (R–FBP), have been investigated as potential materials for the removal of such pollutants. In this study, R–FBP and their corresponding physical and chemically activated carbon (P-RFB-AC and C-FBP-AC) were synthesized using H3PO4 acid and characterized using FT-IR, and SEM analyses. An optimization process was conducted to determine the optimum conditions for achieving high
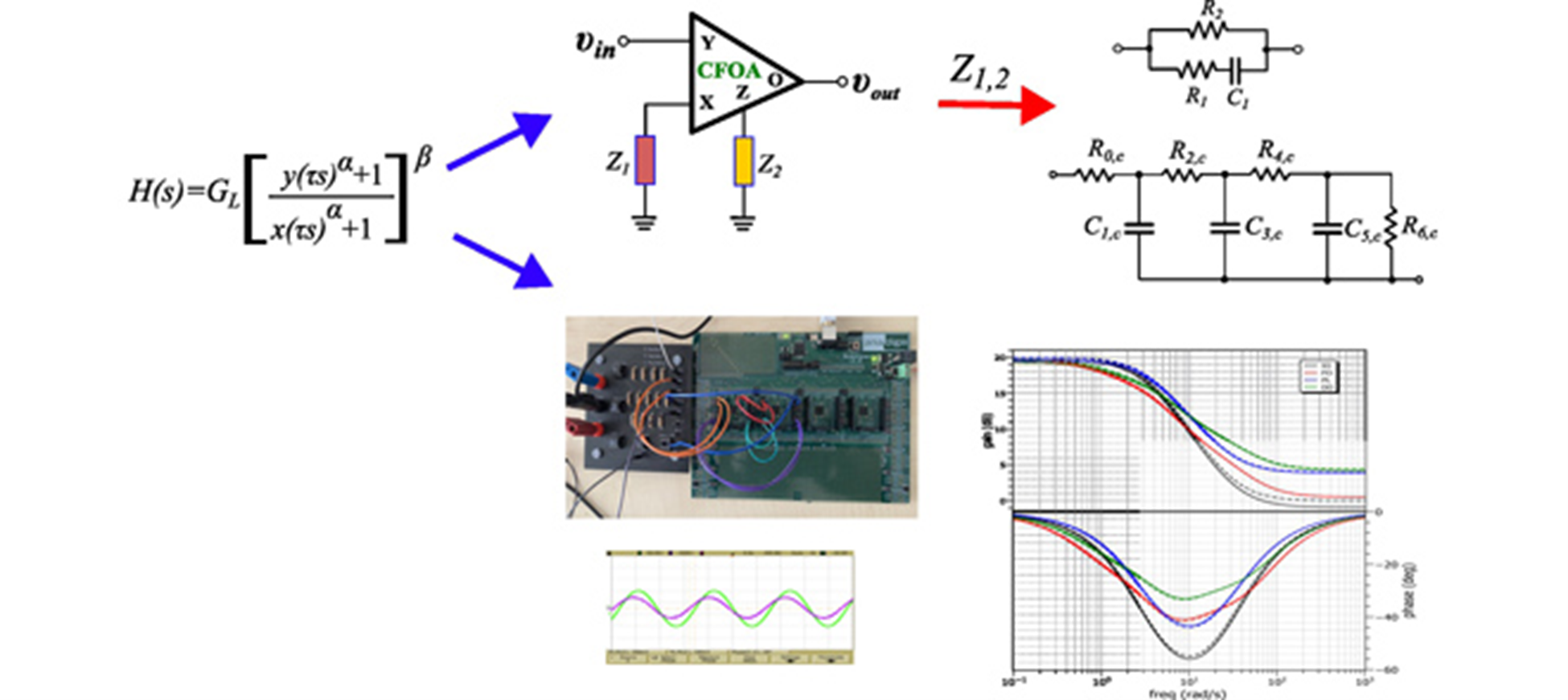
Bilinear Double-Order Filter Designs and Application Examples
A novel kind of non-integer order bilinear filters, named double-order bilinear filters, is introduced in this work. They are based on the employment of two non-integer orders, offering the maximum design flexibility in comparison with their fractional-order and power-law counterparts. An attractive offered benefit is that this is achieved without increasing the circuit complexity, since the proposed structure is capable of realizing all non-integer kinds of filters. Two design examples are provided, where it is shown that lead/lag compensators utilized in control applications and low/high
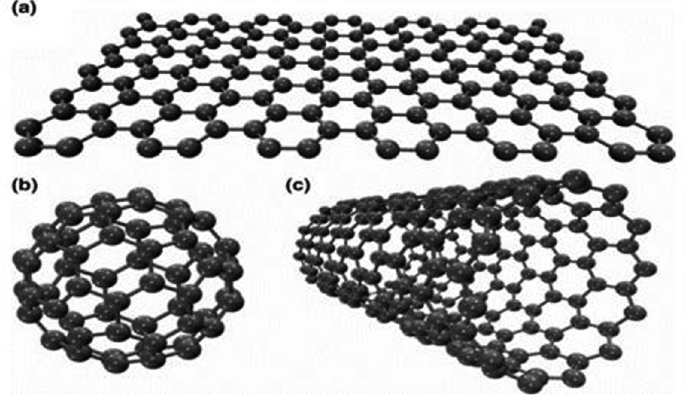
Carbon Nanomaterials and Their Composites as Adsorbents
Carbon nanomaterials with various nanostructures (carbon nanotubes, graphene, graphene oxide, fullerene, nano diamonds, carbon quantum dots, carbon nanofibers, graphitic carbon nitrides, and nano porous carbons) are the decade’s most distinguishing and popular materials. They have distinctive physicochemical qualities such as chemical stability, mechanical strength, hardness, thermal and electrical conductivities, and so on. Furthermore, they are easily surface functionalized and tweaked, modifying them for high-end specific applications. Carbon nanostructures’ properties and surface
Valorization of Agricultural and Marine Waste for Fabrication of Bio-Adsorbent Sheets
Industrial wastewater often contains considerable amounts of toxic pollutants that would endanger public health and the environment. In developing countries, these toxins are often discharged into natural ecosystems without pretreatment as it requires costly treatment processes, which causes long-term harmful socioeconomic impacts. Employing wastewater treatment plants using physical, biological, and chemical methods to clean the wastewater is considered by many nations the answer to the environmental crises. The treated water could be used for targeting the irrigation systems in its majority
Full Connectivity Driven K-LEACH Algorithm for Efficient Data Forwarding in Wireless Sensor Networks
Due to the usage of Internet in everything in our life, our environment is transformed into digital society, in which everything can be accessed from anywhere. This is the main concept of Internet of Things (IoT), which consists of intelligent devices connected together without location limitation. These devices can be sensors and actuators, which are used in environmental monitoring, home automation, disaster management and more. This is the definition of Wireless Sensor Network (WSN), which is considered a subset from IoT environment. WSN consists of hundreds of nodes spread in different
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 7
- Next page ››
