Breadcrumb
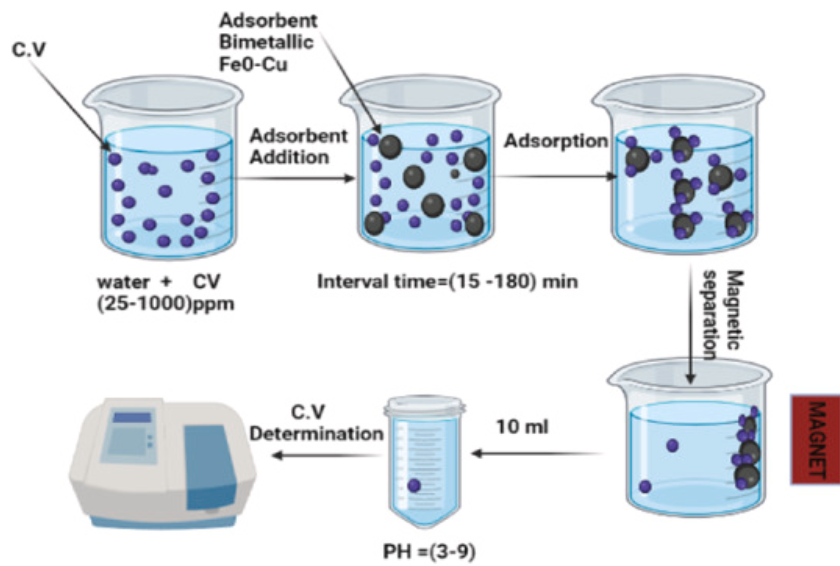
Crystal violet removal using bimetallic Fe0–Cu and its composites with fava bean activated carbon
Nano zero-valent iron (nZVI), bimetallic nano zero-valent iron-copper (Fe0– Cu), and fava bean activated carbon-supported bimetallic nano zero-valent iron-copper (AC-Fe0-Cu) are synthesized and characterized using DLS, zeta potential, FT-IR, XRD, and SEM. The maximum removal capacity is demonstrated by bimetallic Fe0–Cu, which is estimated at 413.98 mg/g capacity at pH 7, 180 min of contact duration, 120 rpm shaking speed, ambient temperature, 100 ppm of C.V. dye solution, and 1 g/l dosage. The elimination capability of the H2SO4 chemical AC-Fe0-Cu adsorbent is 415.32 mg/g under the same
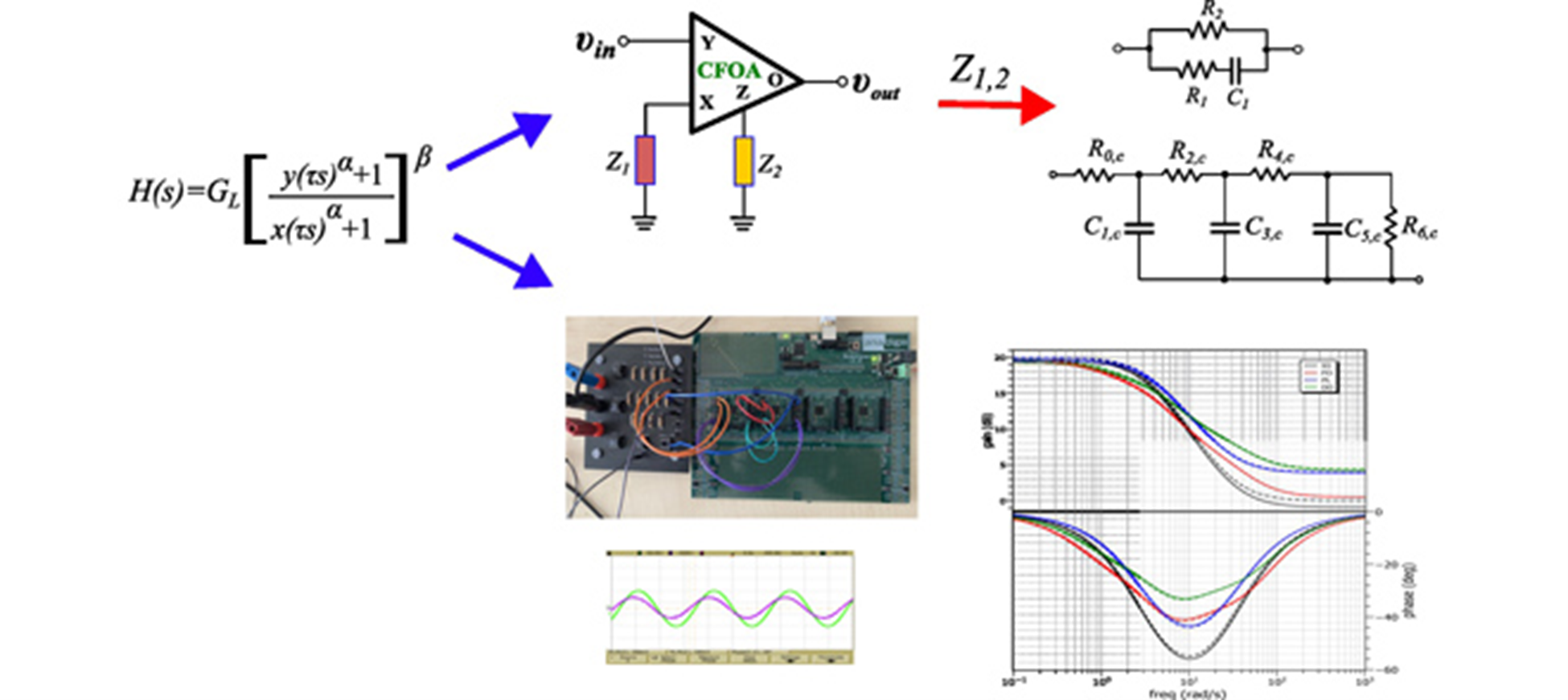
Bilinear Double-Order Filter Designs and Application Examples
A novel kind of non-integer order bilinear filters, named double-order bilinear filters, is introduced in this work. They are based on the employment of two non-integer orders, offering the maximum design flexibility in comparison with their fractional-order and power-law counterparts. An attractive offered benefit is that this is achieved without increasing the circuit complexity, since the proposed structure is capable of realizing all non-integer kinds of filters. Two design examples are provided, where it is shown that lead/lag compensators utilized in control applications and low/high
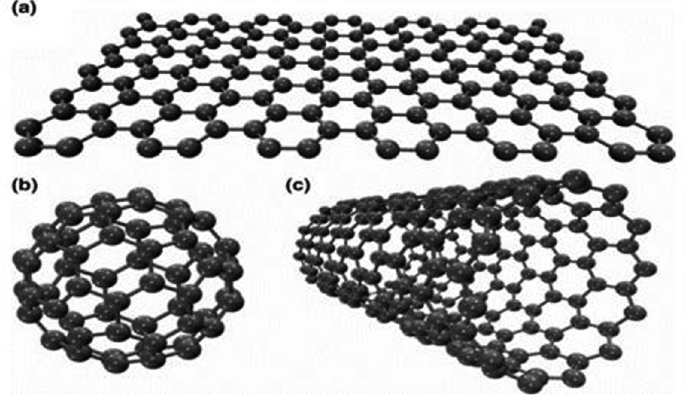
Carbon Nanomaterials and Their Composites as Adsorbents
Carbon nanomaterials with various nanostructures (carbon nanotubes, graphene, graphene oxide, fullerene, nano diamonds, carbon quantum dots, carbon nanofibers, graphitic carbon nitrides, and nano porous carbons) are the decade’s most distinguishing and popular materials. They have distinctive physicochemical qualities such as chemical stability, mechanical strength, hardness, thermal and electrical conductivities, and so on. Furthermore, they are easily surface functionalized and tweaked, modifying them for high-end specific applications. Carbon nanostructures’ properties and surface
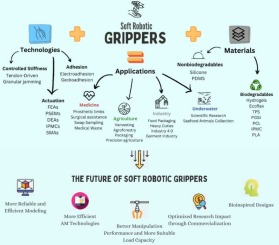
Soft robotic grippers: A review on technologies, materials, and applications
The growing need for manipulators capable of handling delicate objects with care and coexisting safely with humans has brought soft robots to the forefront as a practical and cost-effective solution. In this context, this paper aims to explore soft grippers, a unique and versatile subset of soft robots. It provides an overview of various soft grasping techniques and materials, highlighting their respective advantages and limitations, along with showcasing several designed and tested models. As medicine and agriculture are acknowledged as pivotal domains required for basic human survival, this

Review on Coral Reef Regeneration Methods through Renewable Powered Electrotherapy
The restoration of coral reef population in coastal regions is currently a growing concern. Many attempts have been made to apply new approaches to limit the deterioration of coral reefs, and to accelerate the growth of new reefs to protect coastal areas and ecosystems using available renewable energy sources. This paper highlights the new approaches and their various advantages and limitations in tidal and wave energy. The paper also suggests improvements to some of those systems using the recent developments in soft robotics, especially the use of biomimetic fish as a feasible support
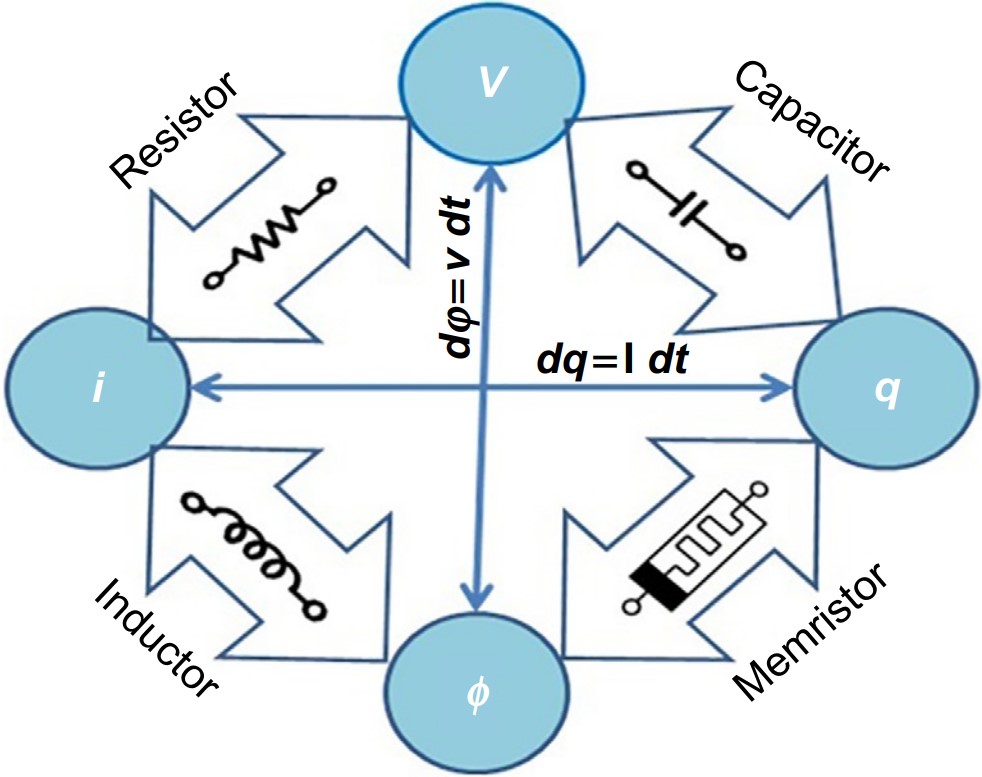
Memristive Fractional-Order Nonlinear Model for Circuit Design
The main objective of this chapter is to bring together studies addressing the current research and history of memristive device evolution available in the literature. The chapter highlights the methodologies and frameworks relevant to the development of nonlinear memristor models suitable for future nanoscale circuit design. An elaborate study of memristor device physics, structure, operation, mathematical modeling, and TCAD simulations is carried out for better understanding of nonlinear models of memristive devices. The memristive device features and content related to memristor nonlinear
Di- and tri- cyclic aromatic hydrocarbons removal using different prepared materials based Sargassum dentifolium algae, and iron oxide
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are highly toxic and carcinogenic compounds as they are low water solubility, hardly degradable and may persist in the environment for many years. Therefore, this study was directed to PAHs ‘anthracene and naphthalene’ removal using a combination method between adsorption and degradation using sunlight. Three adsorbent materials, iron oxide (Fe) alone, Sargassum dentifolium (S) alone, and mixture of Iron oxide and Sargassum dentifolium (FeS) were prepared. Afterwards, optimisation process was performed for the three adsorbent forms through some
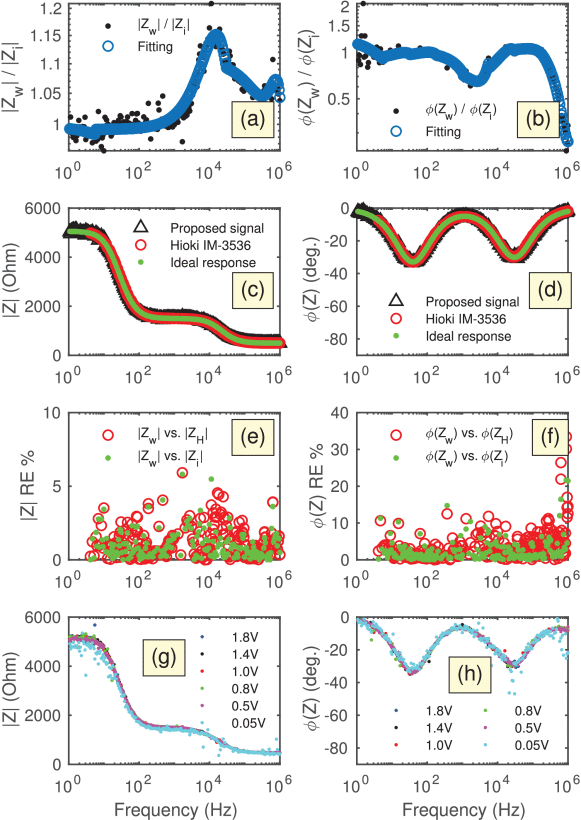
Time-Frequency Design of a Multi-Sine Excitation with Random Phase and Controllable Amplitude for (Bio) Impedance Measurements
Impedance spectroscopy has become a standard electroanalytical technique to study (bio)electrochemical and physiological systems. From an instrumentation point of view, the measurement of impedance can be carried out either in the frequency domain using the classical frequency sweep method or in the time domain using a variety of broadband signals. While time-domain techniques can be implemented with relatively simple hardware and can achieve faster acquisition time, they are still not that popular because of their lower accuracy and modularity. In this work we present a method and an

A collection of interdisciplinary applications of fractional-order circuits
An attractive feature of fractional calculus is its application in various interdisciplinary fields, extending from biomedical and biological notions to mechanical properties. For their description, fractional-order models have outperformed the corresponding integer-order models, resulting in a more realistic behavior, due to the additional degrees of freedom offered and the long-term memory effect that reflects the fractional order. These improved features are processed by appropriate circuit implementations, derived through several approximation methods, whose primary objective is to provide
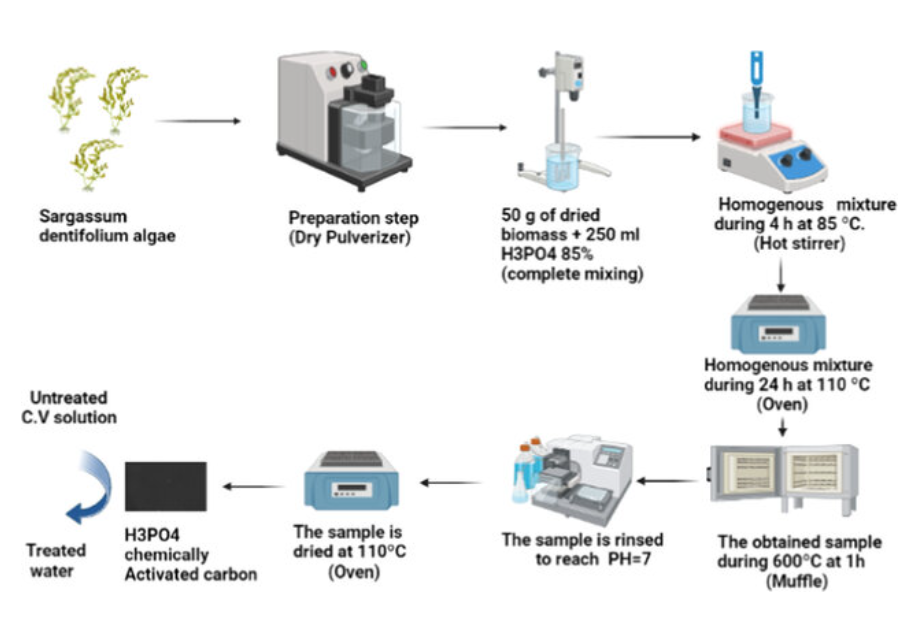
Crystal violet removal using algae-based activated carbon and its composites with bimetallic Fe0-Cu
The textile industry is considered a source of pollution because of the discharge of dye wastewater. The dye wastewater effluent has a significant impact on the aquatic environment. According to the World Bank, textile dyeing, and treatment contribute 17 to 20% of the pollution of water. This paper aims to prepare the bimetallic nano zero-valent iron-copper (Fe0-Cu), algae-activated carbon, and their composites (AC-Fe0-Cu), which are employed as adsorbents. In this paper, Synthetic adsorbents are prepared and examined for the adsorption and removal of soluble cationic crystal violet (CV) dye
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 7
- Next page ››
