Breadcrumb

IOT-based air quality monitoring system for agriculture
Air quality assessment has been discussed for urban environments with a high degree of industrialization, as they are infested with hazardous chemicals and airborne pollutants. The assessment is carried out by monitoring stations, that basically support limited areas while leaving large geographical areas uncovered. The expansion in the agriculture sector directed us towards air quality assessment on the farms. This is because research has shown that crops can be injured when exposed to high concentrations of various air pollutants, while also affecting farmers' health states. But those air
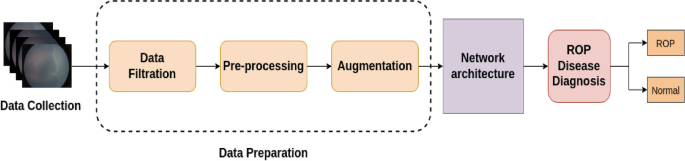
A Robust Deep Learning Detection Approach for Retinopathy of Prematurity
Retinal retinopathy of prematurity (ROP), an abnormal blood vessel formation, can occur in a baby who was born early or with a low birth weight. It is one of the primary causes of newborn blindness globally. Early detection of ROP is critical for slowing and stopping the progression of ROP-related vision impairment which leads to blindness. ROP is a relatively unknown condition, even among medical professionals. Due to this, the dataset for ROP is infrequently accessible and typically extremely unbalanced in terms of the ratio of negative to positive images and the ratio of each stage of it
Threshold Energy Based LEACH-K Effect on the Accessibility of Wireless Sensor Networks
This paper aims to deliver an exhaustive investigation on the threshold energy parameter's direct impact on the Cluster Head (CH) selection phase in Low-Energy Adaptive Clustering Hierarchy Based on K-Means (LEACH-K) protocols. The most prominent threshold energy selection criterion out of the scarcely available research on the LEACH-K threshold energy parameter is used to simulate the LEACH-K protocol. Simulations are carried out on scaled-up Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) in terms of size and number of nodes. An analysis is performed on the life-cycle of the CH selection process, which

Optimization of Double fractional-order Image Enhancement System
Image enhancement is a vital process that serves as a tool for improving the quality of a lot of real-life applications. Fractional calculus can be utilized in enhancing images using fractional order kernels, adding more controllability to the system, due to the flexible choice of the fractional order parameter, which adds extra degrees of freedom. The proposed system merges two fractional order kernels which helps in image enhancement techniques, and the contribution of this work is based on the study of how to optimize this process. The optimization of the two fractional kernels was done
Applications of continuous-time fractional order chaotic systems
The study of nonlinear systems and chaos is of great importance to science and engineering mainly because real systems are inherently nonlinear and linearization is only valid near the operating point. The interest in chaos was increased when Lorenz accidentally discovered the sensitivity to initial condition during his simulation work on weather prediction. When a nonlinear system is exhibiting deterministic chaos, it is very difficult to predict its response under external disturbances. This behavior is a double-edged weapon. From a control and synchronization point of view, this proposes a

Double Visual Cryptography Using Generalized Tent Map, Rotation, and Image Filtering
This paper introduces a Multi-Visual Cryptography (MVC) system for sharing two color images, where the secrets can be revealed with low computation power using all the shares. The system uses the generalized Tent map as a source of randomness to generate any number of random shares. More specifically, (n-1) random shares are generated, and then, the nth share is calculated from the random shares and the secrets using rotations of the shares. In recovery, rotation of the last share recovers the two images based on the angle of rotation. Half the number of pixels is recovered for each secret

Battery Modeling with Mittag-Leffler Function
In various areas of life, rechargeable lithium-ion batteries are the technology of choice. Equivalent circuit models are utilized extensively in characterizing and modeling energy storage systems. In real-time applications, several generic-based battery models are created to simulate the battery's charging and discharging behavior more accurately. In this work, we present two generic battery models based on Mittag-Leffler function using a generic Standard battery model as a reference. These models are intended to fit the continuous discharging cycles of lithium-ion, Nickel-cadmium, and Nickel

Hardware Realization of High-Speed Area-Efficient Floating Point Arithmetic Unit on FPGA
Floating point representations are required in many applications due to their universality and ability to represent huge numbers accurately and in compact bit-width. Floating point arithmetic is complex, performance inefficient, and area-consuming compared to integer arithmetic operations. In this paper, hardware realization of area-efficient high-performance floating point arithmetic units for IEEE 754 floating point single precision and double precision formats on FPGA are proposed. The proposed units achieved the same accuracy as software in all tested cases and were able to produce the
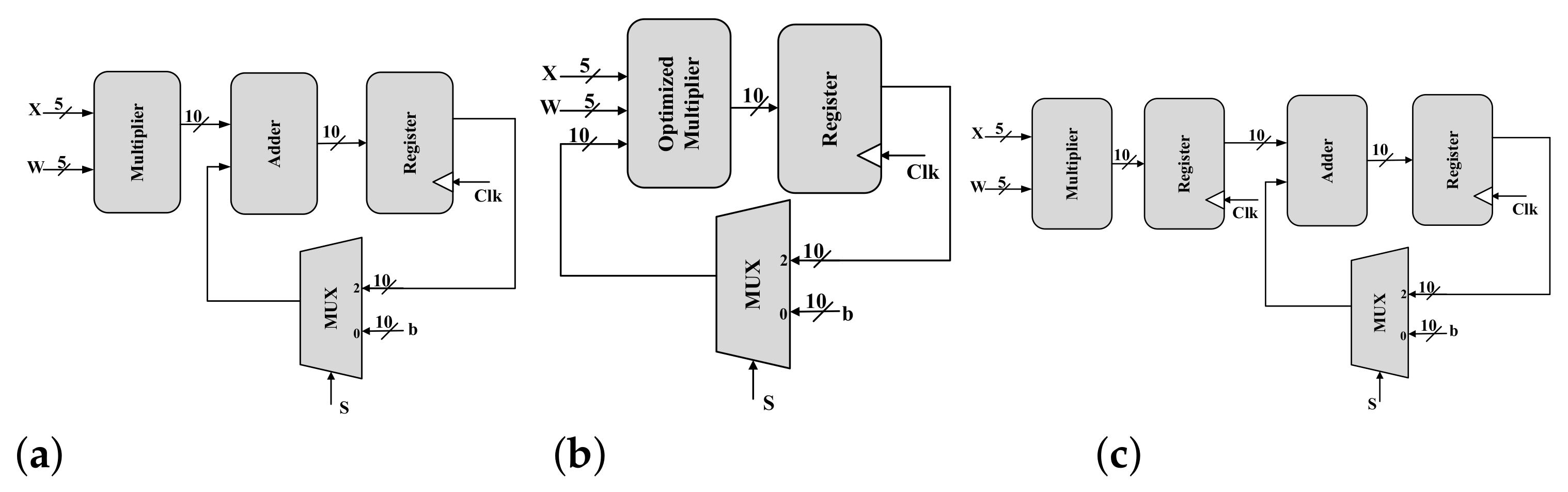
CNTFET-Based Ternary Multiply-and-Accumulate Unit
Multiply-Accumulate (MAC) is one of the most commonly used operations in modern computing systems due to its use in matrix multiplication, signal processing, and in new applications such as machine learning and deep neural networks. Ternary number system offers higher information processing within the same number of digits when compared to binary systems. In this paper, a MAC is proposed using a CNTFET-based ternary logic number. Specifically, we build a 5-trit multiplier and 10-trit adder as building blocks of two ternary MAC unit designs. The first is a basic MAC which has two methods to

Artificial Neural Network Chaotic PRNG and simple encryption on FPGA
Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) are remarkably able to fit complex functions, making them useful in various applications and systems. This paper uses ANN to fit the Pehlivan–Uyaroglu Chaotic System (PUCS) to produce an Artificial Neural Network Chaotic Pseudo-Random Number Generator (ANNC-PRNG). The proposed PRNG imitates the PUCS chaotic system's properties and attractor shape. The proposed ANNC-PRNG is implemented in a simple image encryption system on the Xilinx Kintex-7 Genesys 2 Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) board. Hardware realization of an ANN trained on chaotic time series has
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 4
- Next page ››
