Breadcrumb
An Efficient DMO Task Scheduling Technique for Wearable Biomedical Devices
The popularity of wearable devices has grown as they improve the quality of life in many applications. In particular, for medical devices, energy harvesters are the dominating source of energy for wearable devices. However, their power budget is limited. Thus, power-saving techniques are essential components in the whole technology stack of those devices. That is, choosing the optimal schedule for different tasks running on the wearable device can help to reduce energy consumption. This paper presents a sensor task scheduling technique for optimizing energy consumption for energy harvesting
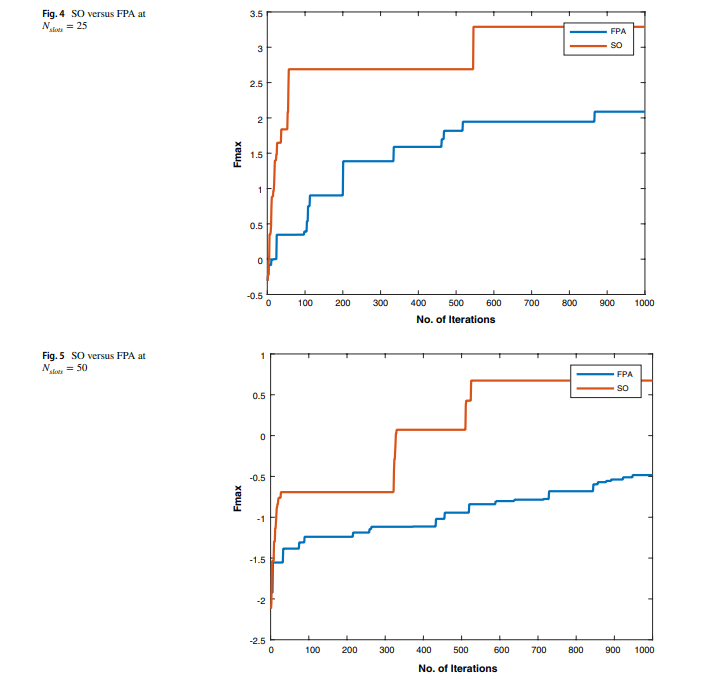
A power-aware task scheduler for energy harvesting-based wearable biomedical systems using snake optimizer
There is an increasing interest in energy harvesting for wearable biomedical devices. This requires power conservation and management to ensure long-term and steady operation. Hence, task scheduling algorithms will be used throughout this work to provide a reliable solution to minimize energy consumption while considering the system operation constraints. This study proposes a novel power-aware task scheduler to manage system operations. For example, we used the scheduler to handle system operations, including heart rate and temperature sensors. Two optimization techniques have been used to

Modified Blowfish Algorithm Based on Improved Lorenz Attractor
Image security becomes important topic because of increasing image usage in communication besides assures information security which is unseen in these images such as military and medical images. Blowfish is a superb symmetric cryptography that ensures a high degree of resistance to attacks. The proposed system modifies Blowfish algorithm by substituting the function in blowfish round with light weight function to save memory and resources of the platforms and Using 3-D chaotic system (Improved Lorenz) that work as a key timetable for creating Blowfish sub keys in order to increasing
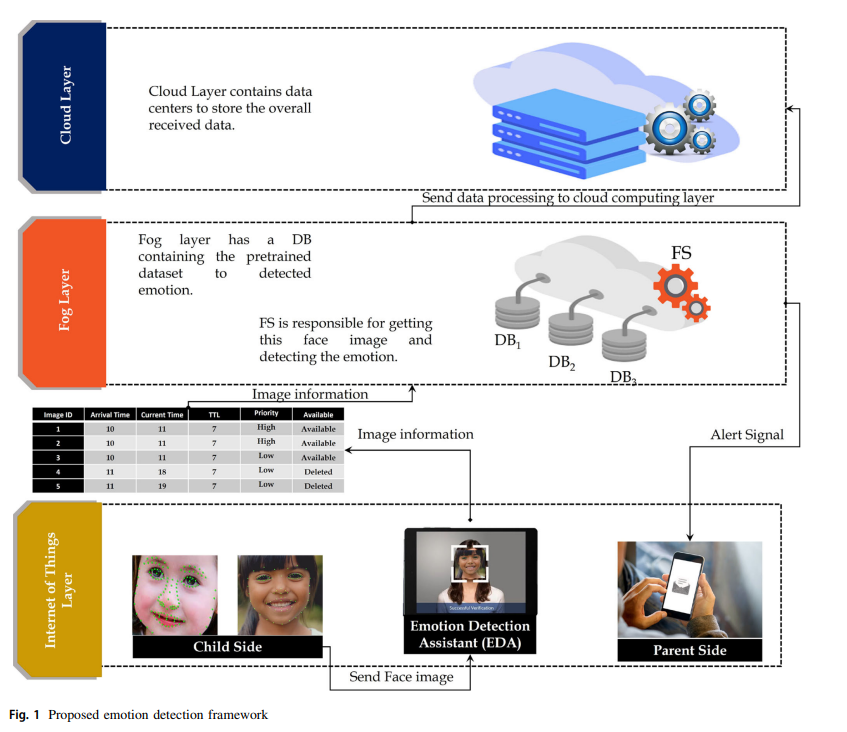
Real-time facial emotion recognition model based on kernel autoencoder and convolutional neural network for autism children
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder that is characterized by abnormalities in the brain, leading to difficulties in social interaction and communication, as well as learning and attention. Early diagnosis of ASD is challenging as it mainly relies on detecting abnormalities in brain function, which may not be evident in the early stages of the disorder. Facial expression analysis has shown promise as an alternative and efficient solution for early diagnosis of ASD, as children with ASD often exhibit distinctive patterns that differentiate them from typically
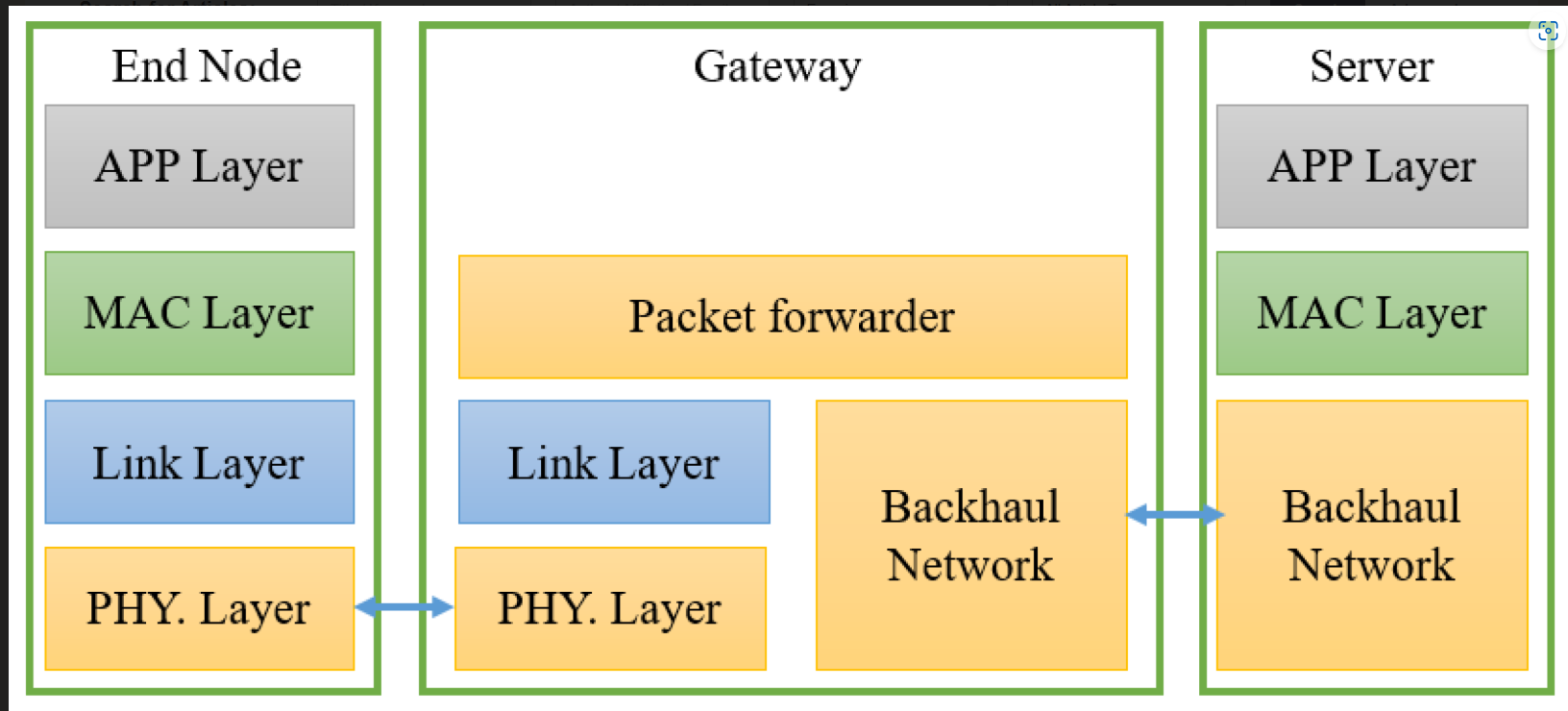
Internet of Things: A Comprehensive Overview on Protocols, Architectures, Technologies, Simulation Tools, and Future Directions
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a global network of interconnected computing, sensing, and networking devices that can exchange data and information via various network protocols. It can connect numerous smart devices thanks to recent advances in wired, wireless, and hybrid technologies. Lightweight IoT protocols can compensate for IoT devices with restricted hardware characteristics in terms of storage, Central Processing Unit (CPU), energy, etc. Hence, it is critical to identify the optimal communication protocol for system architects. This necessitates an evaluation of next-generation
Accelerated Edge Detection Algorithm for High-Speed Applications
Digital Image Processing (DIP) is a growing field for various applications, such as autonomous vehicles and video surveillance. To improve the performance of DIP systems, image processing algorithms are implemented in hardware rather than software. The idea here is primarily to get a faster system than software imaging or other alternative hardware. Field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs) have the advantages of parallel processing, low cost, and low power consumption. These semiconductor devices contain many logic blocks that can be programmed to perform everything from basic digital gate-level

Novel Fast Prediction Algorithm for Advanced and High Efficiency Video Coding
This paper introduces an efficient prediction algorithm tailored for advanced and high efficiency video coding, encompassing both H.264 and H.265. The proposed approach aims at replacing the standard intra prediction methodology by employing a streamlined prediction mode, which significantly reduces computational overhead and system complexity while eliminating the requirement for mode decision. By leveraging block comparison criteria, the designed method combines neighboring blocks in a linear fashion to accurately represent the target block. Extensive comparisons are conducted with the H.264
Small Area and Low Power Hybrid CMOS-Memristor Based FIFO for NoC
Area and power consumption are the main challenges in Network on Chip (NoC). Indeed, First Input First Output (FIFO) memory is the key element in NoC. Increasing the FIFO depth, produces an increas in the performance of NoC but at the cost of area and power consumption. This paper proposes a new hybrid CMOS-Memristor based FIFO architecture that consumes low power and has a small size compared to the conventional CMOS-based FIFOs. The predicted area is approximately equal to the half of that wasted in conventional FIFOs. The implementation of FIFO controller module is implemented using HDL
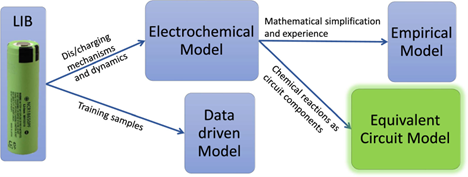
Fractional-Order Equivalent-Circuit Model Identification of Commercial Lithium-Ion Batteries
The precise identification of electrical model parameters of Li-Ion batteries is essential for efficient usage and better prediction of the battery performance. In this work, the model identification performance of two metaheuristic optimization algorithms is compared. The algorithms in comparison are the Marine Predator Algorithm (MPA) and the Partial Reinforcement Optimizer (PRO) to find the optimal model parameter values. Three fractional-order (FO) electrical equivalent circuit models (ECMs) of Li-Ion batteries with different levels of complexity are used to fit the electrochemical
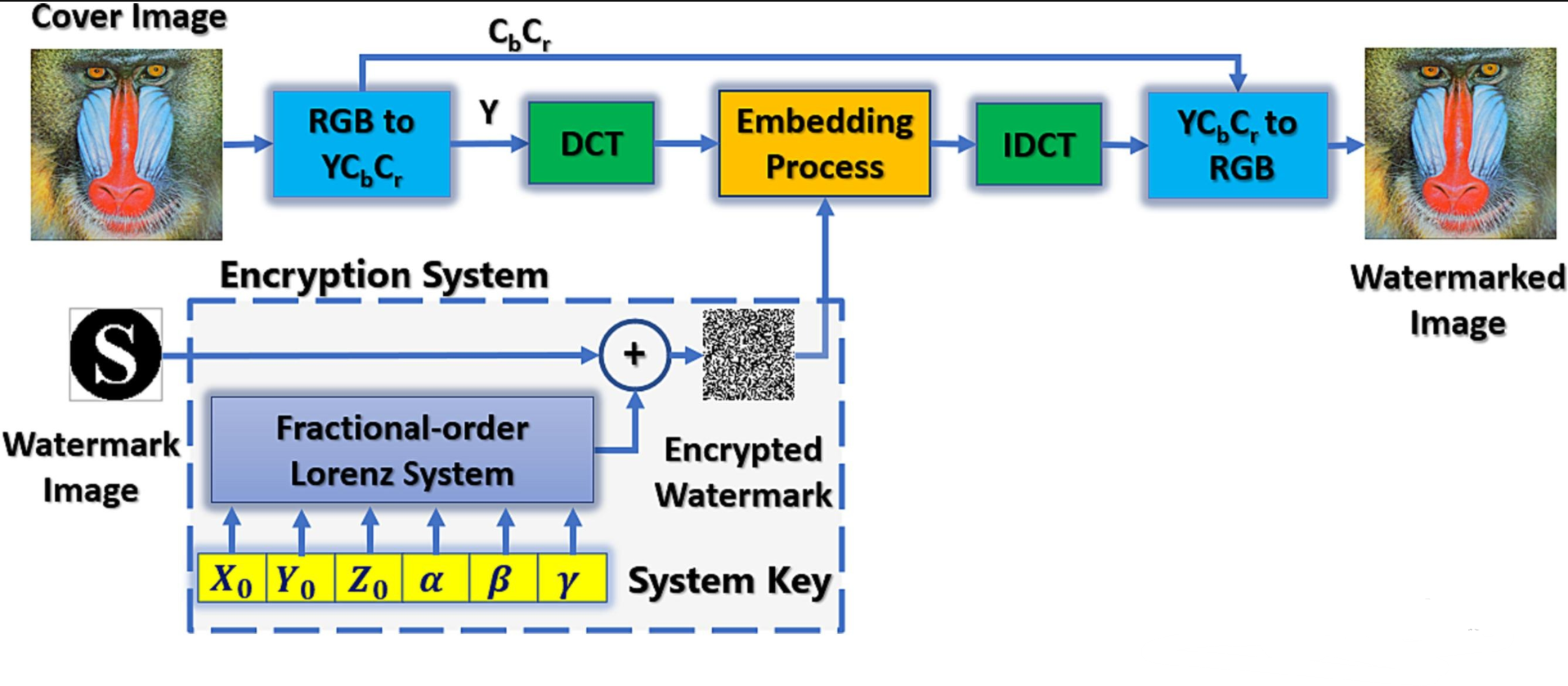
Secure blind watermarking using Fractional-Order Lorenz system in the frequency domain
This paper investigates two different blind watermarking systems in the frequency domain with the development of a Pseudo Random Number Generator (PRNG), based on a fractional-order chaotic system, for watermark encryption. The methodology is based on converting the cover image to the YCbCr color domain and applying two different techniques of frequency transforms, Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT) and Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT), to the Y channel. Then, the encrypted watermark is embedded in the middle-frequency band and HH band coefficients for the DCT and DWT, respectively. For more
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 2
- Next page ››
